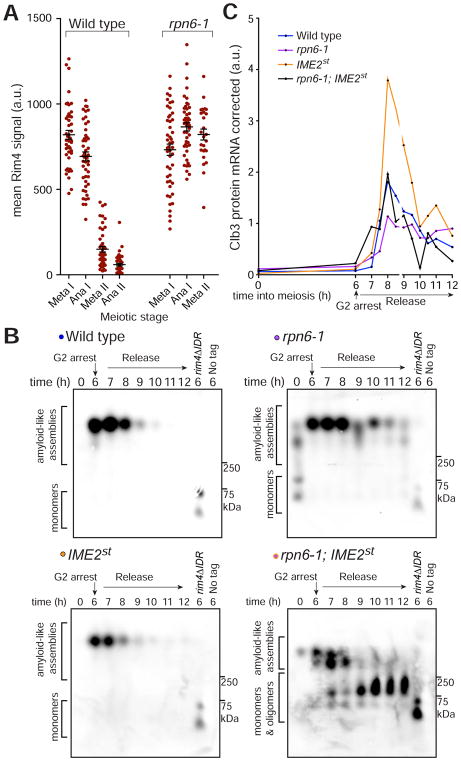
Figure 6. Rim4 assemblies are disassembled prior to proteasomal degradation.
(A) The proteasome is critical for Rim4 clearance. Strains harboring pGAL-NDT80, GAL4.ER, CLB3-3HA, and RIM4-3V5 and either RPN6 (wild type) or rpn6-1 were induced to sporulate at 30°C. After 6 hours, cells were released from the G2 arrest. Single-cell Rim4 levels in metaphase I, anaphase I, metaphase II, and anaphase II were determined by immunofluorescence (IF) (n = 48 for each meiotic stage except rpn6-1 metaphase II in which n = 26 and anaphase II in which n = 0). CLB3 translational control and meiotic progression analysis is shown in Figures S6A, S6B.
(B, C) Strains harboring pGAL-NDT80, GAL4.ER, CLB3-3HA, RIM4-3V5 and either RPN6 (wild type, blue, B48), rpn6-1 (purple, B207), IME2st (yellow, A33024), or rpn6-1; IME2st (black, B251) were grown as in (A). (B) Rim4 SDS-resistant assemblies were analyzed by SDD-AGE. (C) CLB3 translational control analysis. Clb3 protein levels corrected for CLB3 mRNA levels are plotted on the y-axis and time in meiosis is plotted on the x-axis. Quantification of mRNA-corrected Clb3 protein levels is shown. Source data and meiotic progression analysis is shown in Figures S6C, S6D.