Fig. 2. Production of a microfluidic device using 3D printing of sugar glass.
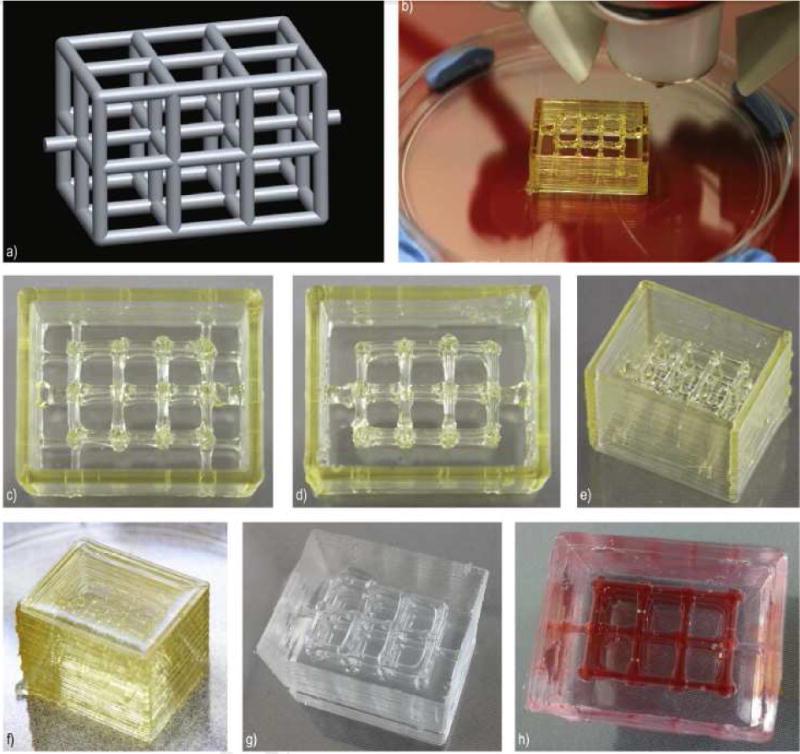
a) CAD model of the desired microfluidic channel. b) Device in the process of printing. c–e) Completed view of the sugar glass structure. f) Sugar glass structure after casting in PDMS g) microfluidic chambers after casting with PDMS and dissolution of sugar glass channels. h) Red Dye added for channel visualization. Image reproduced, with permission, from reference 25.
