Figure 7. Gp120 enhancement of EPSCNR2AR and EPSCNR2BR.
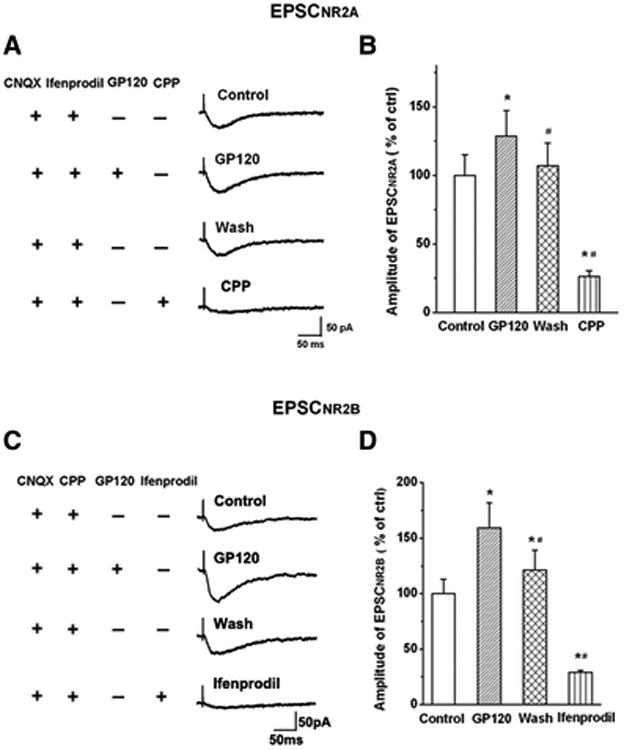
A. EPSCNR2AR was isolated by addition of AMPAR antagonist CNQX (10μM) and NR2BR antagonist ifenprodil (10μM) to the perfusate. Exemplary EPSCNR2AR traces were recorded in a CA1 neuronal cell before (Ctrl), during (gp120), after (washout) bath perfusion of gp120, and subsequent pharmacological confirmation of EPSCNR2AR by a specific NR2AR blocker R-CPP (CPP). Note that bath perfusion of gp120 increased EPSCNR2A and the EPSCNR2A returned to control level after washout of gp120. Addition of R-CPP almost completely blocked EPSCNR2A, demonstrating the pharmacologically isolated EPSCs were EPSCNR2AR. B. EPSCNR2BR was isolated with the addition of AMPAR antagonist CNQX (10μM) and NR2AR antagonist R-CPP (1μM) to the perfusate. Exemplary EPSCNR2BR traces were recorded from another CA1 neuronal cell before (Ctrl), during (gp120), after (washout) bath perfusion of gp120, and pharmacological confirmation of EPSCNR2BR by a specific NR2BR blocker ifenprodil (Ifenprodil). B and D are summary bar graphs showing average amplitudes (% of control) of EPSCnr2ar (B) and EPSCNR2BR (D) recorded under various experimental conditions as indicated, respectively. Note that gp120 enhanced both EPSCNR2AR (128.61±18.64% of control, n=11, M±SD) and EPSCNR2BR (159.25±22.77% of control, n=8, M±SD) with a significant stronger effect (t(17)=0.0046; p<0.01) on enhancing EPSCNR2BR and EPSCNR2AR. * p<0.05 vs control; # p<0.05 vs gp120 group.
