Figure 8. gp120 interacts with extrasynaptic NR2BRs (exNR2BRs).
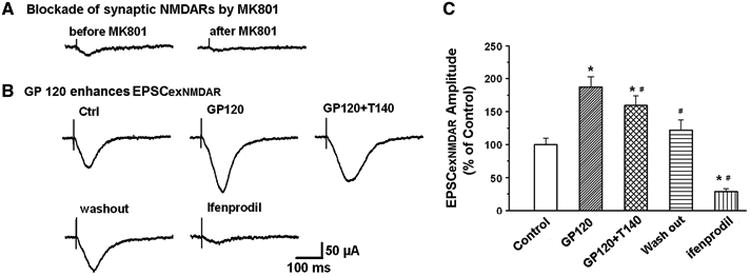
A. Blockade of synaptic EPSCNMDAR by MK801 (70μM, an open NMDAR channel blocker)combined with a 10min low frequency (0.05Hz) stimulation of Schaffer-collateral fiber protocol. B. Exemplary EPSCNMDAR traces recorded in different experimental conditions after synaptic NMDARs were blocked by MK801 as shown in A. Note addition of gp120 enhanced EPSCNMDAR which was most likely mediated via an interaction with extrasynaptic NMDARs. Since NMDARs in the hippocampus are composed mainly of NR2ARs and NR2BRs, the enhancement of EPSCNMDAR by gp120 under the blockade of synaptic NMDARs (predominantly NR2ARSs) suggests that gp120 may act most on exNR2BRs. This suggestion was supported by the experimental results that addition of ifenprodil, a specific NR2BR antagonist, blocked EPSCNMDAR, demonstrating gp120 enhancement of EPSCexNR2BR. The gp120-mediated enhancement of EPSCexNR2BR was attenuated by T140, indicating gp120 interacts with CXCR4. C. Average EPSCexNR2BR recorded under different experimental conditions as indicated in panel B. Note a significant enhancement of EPSCexNR2BR by gp120 and its attenuation by a CXCR4 receptor blocker T140. These results illustrate that gp120 acts on exNR2BRs. n=8, *p<0.05 vs control, #p<0.05 vs gp120.
