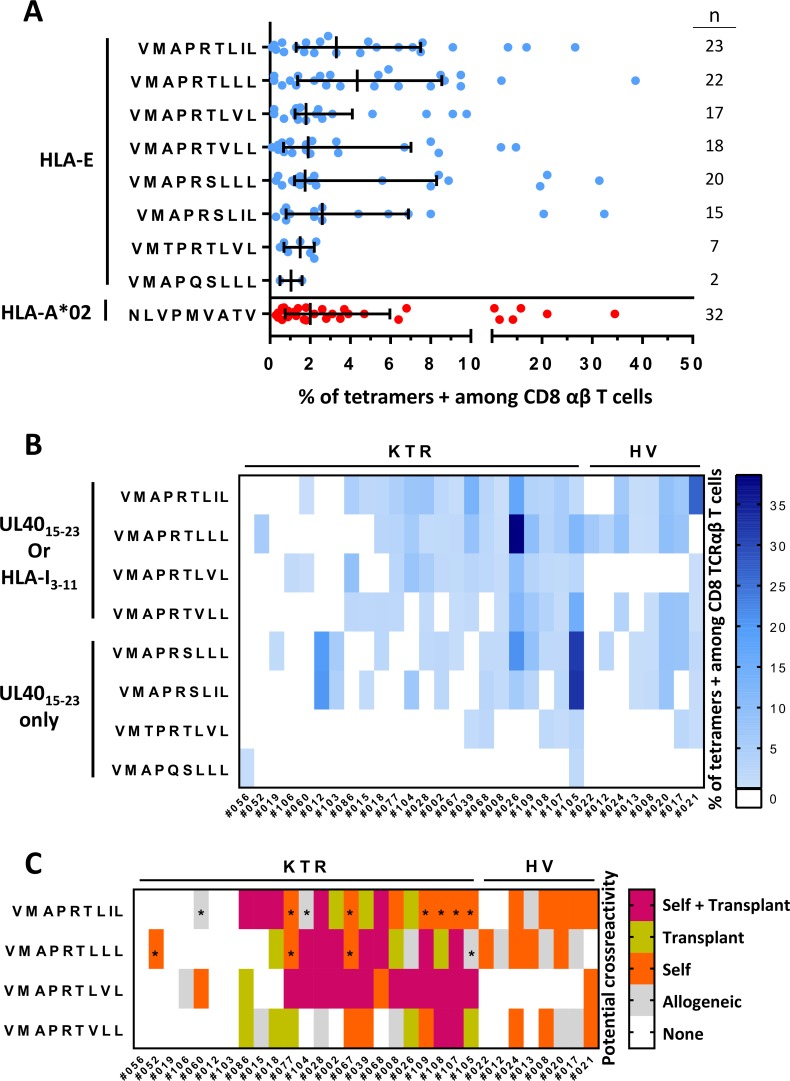
Fig 6. Potential cross-recognition of autologous and allogeneic HLA-I signal peptides by HLA-EUL40 CD8 T cells.
PBMCs were isolated from freshly or prospectively collected blood samples at M12 post-transplantation issued from healthy donors (HV, n = 25) or from kidney transplant recipients (KTR, n = 119), respectively. Ex vivo detection of HLA-EUL40 CD8 T and HLA-A*02pp65-specific CD8 T cells was performed using flow cytometry by selecting CD3+ CD8α+ TCRγδ- tetramer+ cells on PBMCs. Eight different HLA-EUL40 tetramers were used independently. (A) Percentage of circulating anti-HCMV CD8 T cells in blood detected using the various HLA-EUL40 (blue) and HLA-A*02pp65 (in red) tetramers in HV and KTR. For each tetramer/peptide, the number of individuals with a given CD8 T-cell response is indicated. (B) Diversity and magnitude of the HLA-EUL40 CD8 T-cell responses in KTR and HV. HLA-EUL40 CD8 T-cell responses appear in blue and colour intensity is proportional to the percentage of HLA-EUL40 CD8 T cells. (C) Classification of the HLA-EUL40 CD8 T-cell responses in HCMV+ hosts according to possible recognition of self (orange), donor-specific allogeneic (green) or both (violet) (n = 31, 23 KTR and 8 HV). Grey boxes show HLA-I signal peptides which are not derived from the recipient, nor from the donor. Asterisks indicate peptides with underestimated information due to a lack of HLA-C genotyping.