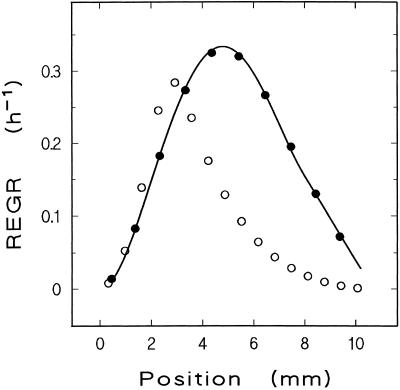
Figure 2.
Methodological test for reliability of REGR profile determination. The test is based on a known REGR profile, from which segment length changes in theoretical marking experiments are computed. From these data, derived REGR profiles are determined by application of the method that is to be tested for reliability. Deviations of the derived profile from the known one indicate systematic errors induced by the method under consideration. The graph gives the known REGR profile as a bold line. Two derived profiles are marked by circles; each symbol represents the relative growth rate of a root segment. In one case, data were created for experimental conditions prevailing in the present study and processed by our method (●; initial segment length 0.9 mm, time between measurements 54 min, segmental relative growth rate plotted versus average segment position), and the agreement with the original profile was excellent. In a second case, alternative experimental conditions and analytical methods as used in a previous study (Pilet et al., 1983) were modeled (○; initial segment length 0.65 mm, time between measurements 6 h, segmental relative growth rate plotted versus initial segment position), resulting in significant distortion of the original profile. The REGR peak is shifted apically by almost 2 mm, the growing zone appears shortened, and the velocity of root elongation (which equals the area under an REGR profile) is reduced by 47%. See text for more details.