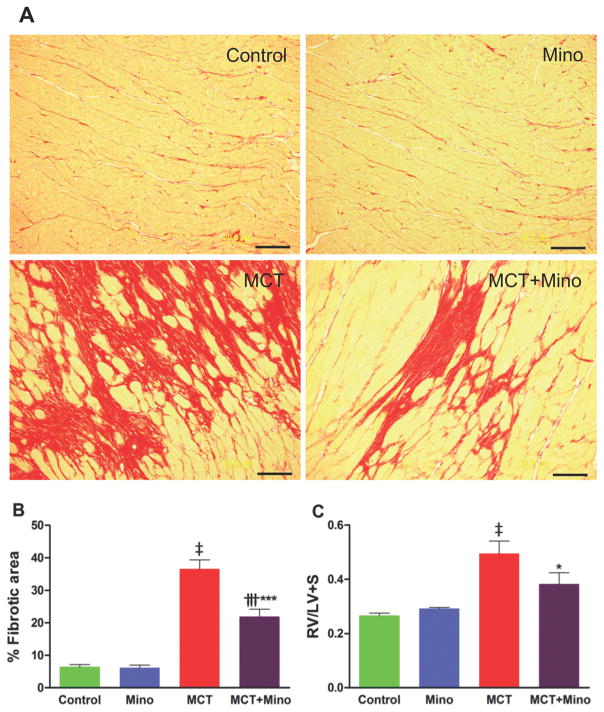
Figure 2. ICV minocycline treatment reduces the RV fibrosis (RVF) and hypertrophy (RVH) induced by MCT.
A, Representative micrographs of collagen stained with Picro Sirius Red revealing increased fibrosis in MCT-treated rats. B, Cumulative analysis of MCT-treated rats shows significant collagen accumulation in the RV indicating the development of fibrosis. C, RVH determined as the ratio of RV to LV and intraventricular septum (S) weight [RV/(LV+S)]. Minocycline treatment exerts anti-fibrotic and anti-hypertrophic effects in the RV of MCT-treated rats. ‡p<0.001 vs. control and minocycline; ***p<0.001, *p<0.05 vs. MCT; †††p<0.001 vs. control and minocycline (n= 5–6 rats/group) (scale bar =20 μm). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls post hoc test. 2-way ANOVA showed significant interaction between MCT and minocycline on RVF (p=0.0016).