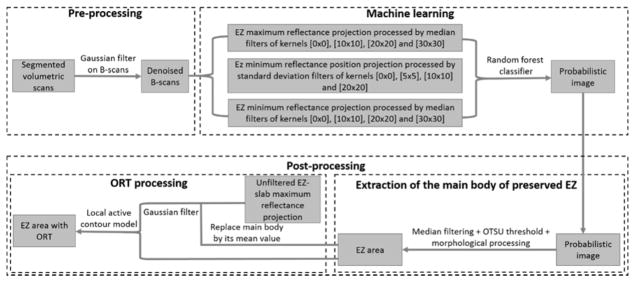
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the preserved ellipsoid zone detection algorithm. A pre-processing step takes the Bruch’s membrane segmentation and denoises by B-scans by application of a Gaussian filter. Then, a random forest classifier formed by 50 decision trees, which has been trained on 12 features of a population of 15 choroideremia eyes and 5 healthy eyes is applied on the scan under scrutiny. A probabilistic map of the main body of preserved ellipsoid zone (EZ) region is generated by the random forest classifier. Outer retinal tubulations (ORT) with the form of pseudopodial extensions protruding from the main body region are not detected by the random forest. To identify them, the main body of preserved EZ is extracted by a filtering step followed by Otsu thresholding. Then, the main body of preserved EZ is identified in the unfiltered maximum reflectance projection and substituted by its mean reflectance value. This image is then filtered and fed into a local active contour routine that extracts the ORT.