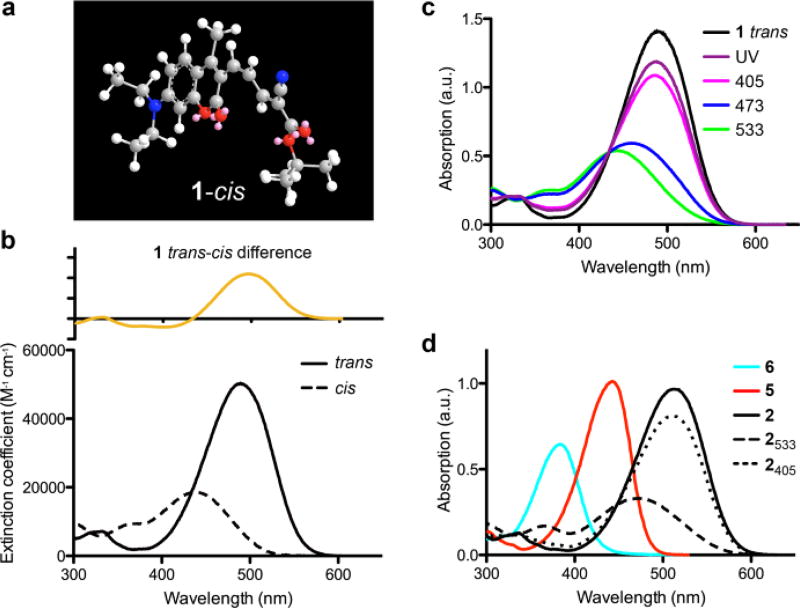
Figure 1.
Structure of cis-ceCAM and UV-visible absorption spectra of ceCAM and related compounds. (a) 3D representation of cis-ceCAM derived from MM2 energy minimization calculations in ChemDraw3D. (b) Absorption spectrum of trans-ceCAM (solid) and calculated absorption spectrum of cis-ceCAM (dashed, ε437 = 18,600 M−1 cm−1) in MeCN with difference spectrum (top). (c) PSS of ceCAM in MeCN using various light sources. (d) Absorption spectra in MeCN of aldehyde 5 (red), locked-ketone 6 (cyan) and trans-dcCAM 2 (black) and PSS spectra from 533 nm (dashes) and 405 nm (dots) laser irradiation of dcCAM.