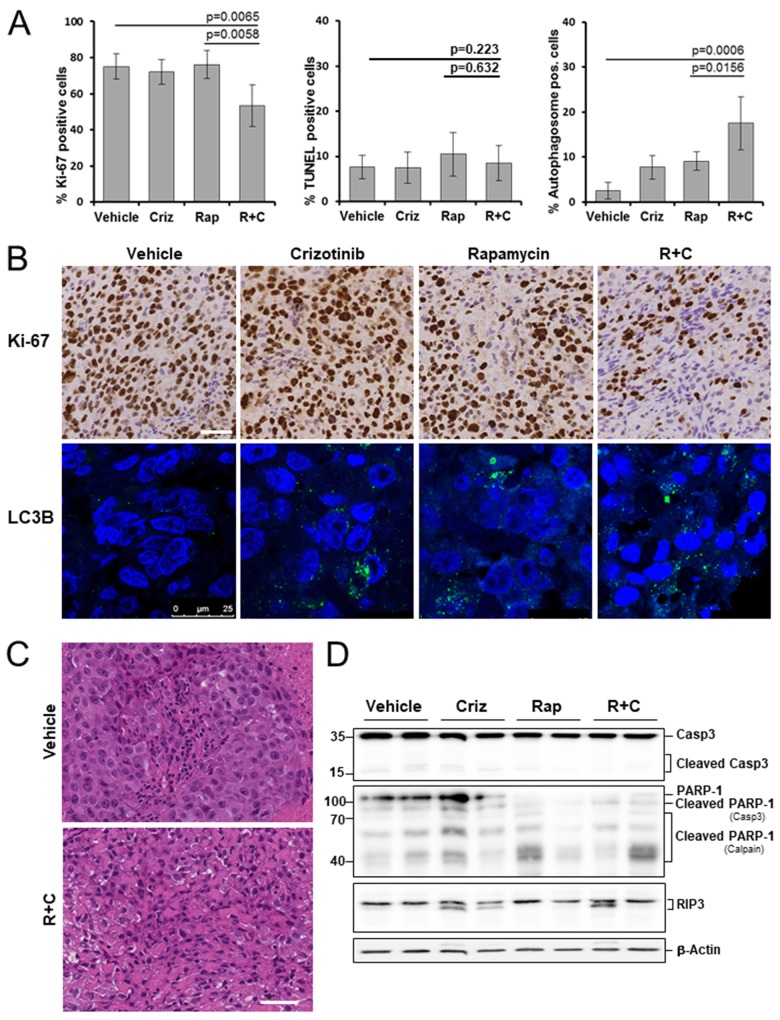
Figure 4. Effects of rapamycin, crizotinib and combined treatment on cell proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy in a mesothelioma xenograft model.
Mice bearing PDX680 xenografts were treated with vehicle, crizotinib (Criz), rapamycin (Rap), or rapamycin and crizotinib (Rap+Criz) for 21 days. (A) Proliferative cells were visualized by immunohistochemical staining with anti-Ki-67, apoptotic cells by TUNEL assay, and autophagy by immunofluorescence monitoring of LC3B incorporation into autophagosomal membranes. Quantification of overall percentage of area positive for Ki-67 (left), TUNEL (middle), LC3B (right). Error bars represent s.d. between individual animals (n=5 per group). (B) Representative immunohistochemical images for Ki-67 (top) and immunofluorescence images for LC3B (bottom) of vehicle and treated samples. (C) Representative H&E images of tumors treated with vehicle or rapamycin and crizotinib. Note vacuolization, chromatin condensation and loss of cell membrane integrity as effects of combined treatment. (D) Immunoblots of PDX680 tumor cells isolated on day 21 after treatment of indicated vehicle or drug (two individual tumors per treatment group). Criz, crizotinib; Rap, rapamycin; R+C, rapamycin and crizotinib; scale bar, 200μm.