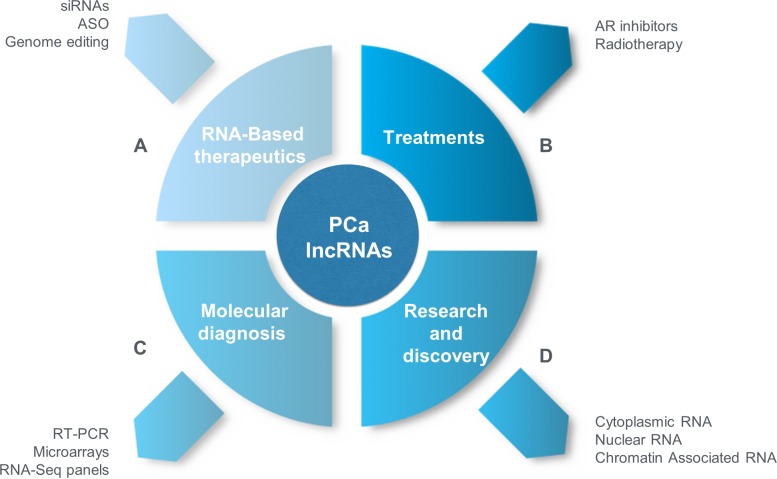
Figure 1. Long non-coding RNAs in PCa and precision medicine.
(A) RNA Based-therapeutics. RNA-based therapeutics, such as siRNAs, ASOs, genome editing by ZFN and the use of regulatory sequence of lncRNAs in recombinant plasmids have great potential to target lncRNAs in PCa to generate entirely new therapeutics in PCa. (B) Treatments. Novel AR signaling inhibitors as enzalutamide has been used to aboard CRPC patients, and targeting lncRNAs trough RNA-based therapeutics strategies can be applied in order to avoid resistance to several drugs, in the future the same one could be applied to radiotherapy where lncRNAs has been proposed as predictive markers of radisensitivity [149–151]. (C) Molecular Diagnosis. lncRNAs can be used as molecular biomarkers in tumor and blood samples (invasive methods) or urine (non-invasive methods) for subsequent detection by qRT-PCR, microarrays, in situ hybridization and RNA-Seq panels for use in personalized treatments and prognosis (e.g., disease recurrence, disease progression, and death). (D) Research and discovery. It will be necessary to determine the different mechanisms by which lncRNAs are associated with the molecular pathogenesis of PCa; using cell lines, biopsies and primary cultures, isolated RNA can be obtained from cellular compartments (cytoplasm and nucleolus) in addition to the chromatin-associated lncRNAs. RNA-Seq will enable discoveries of new lncRNAs that are involved in the development and progression of PCa. These lncRNAs will be useful as new molecular biomarkers for PCa diagnosis, prediction and prognosis.