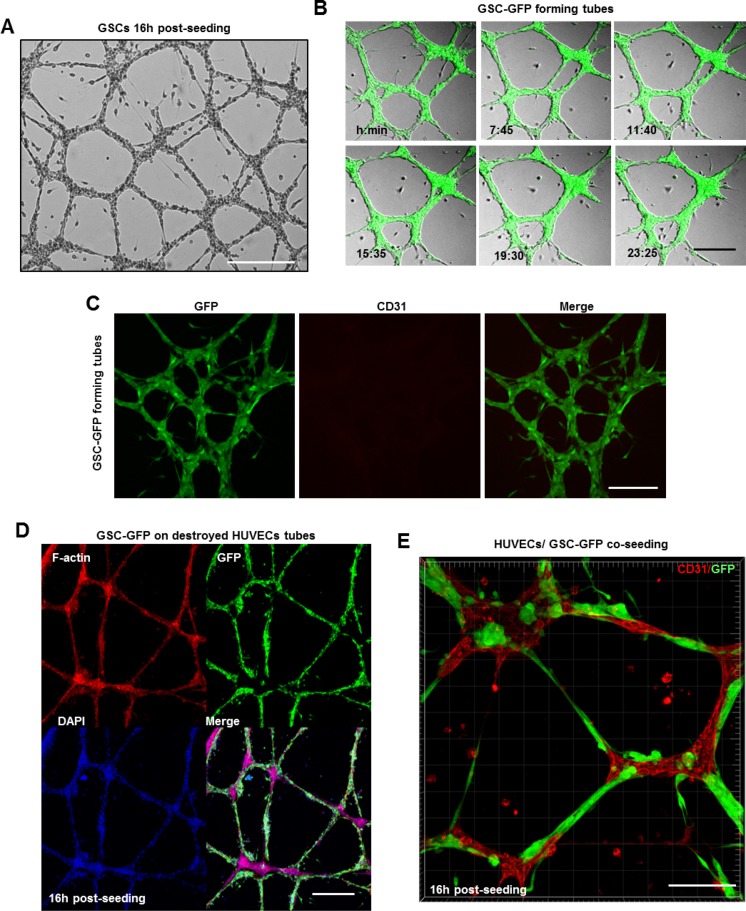
Figure 5. GSCs alone or in cooperation with ECs can contribute to GBM vascularization.
(A) GSCs formed vascular networks reminiscent of normal endothelium over the gelled matrix. (B) Representative images extracted from a time series of GSC-GFP cells forming tubes over the gelled matrix. (C) GSC-derived tubes were fixed and stained with a CD31 antibody (red). GSC cells did not express the endothelial marker CD31. (D) Representative confocal images of GFP expressing GSCs plated on damaged HUVEC-derived tubes and stained for DAPI (blue) and rhodamine phalloidin (red). GSC-GFP cells efficiently restored the destroyed tubes around the HUVEC-remaining branch points. (E) A mixed population of GSC-GFP and HUVEC cells was seeded on a gelled substrate in serum-free neurobasal medium. To discriminate GSCs (green) from HUVECs cells, the tubes were fixed and stained with a CD31 antibody (red). GSCs physically interacted with HUVECs and formed intact vascular tubes. Bars: (A) 100 μm; (B) 50 μm; (C) 50 μm; (D) 50 μm; E) 100 μm.