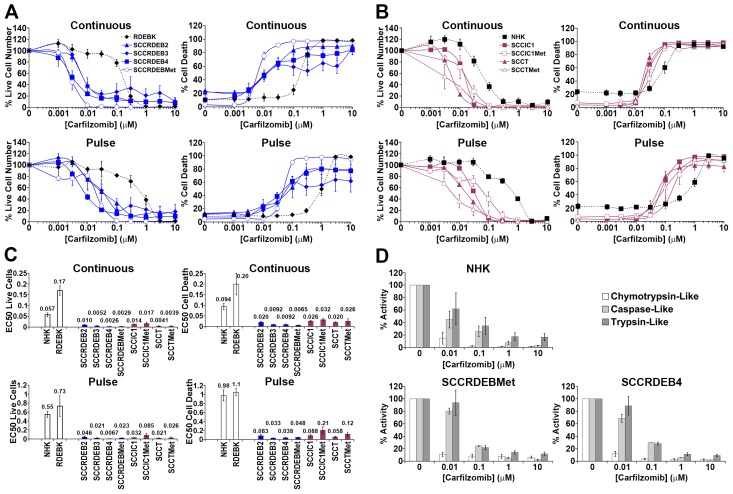
Figure 2. Carfilzomib exhibits more general anti-cSCC selectivity than bortezomib.
(A-C) Cells were continuously incubated with the proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib or treated with an 8-hour carfilzomib pulse. Cell viability (live cell number), expressed as a percentage of carrier alone and the percentage of dead cells were assayed by real-time imaging 72 hours after drug addition. Values are the mean -/+ SEM of 3 independent experiments. (A) Normal keratinocytes and cSCC cell lines from RDEB patients. (B) Normal keratinocytes and cSCC cell lines from: immunocompetent (SCCIC) and transplant (SCCT) patients. (C) Relative EC50 values (μM) for reducing cell viability (live cell number) and for promoting cell death. cSCC cell lines were more sensitive to continuous carfilzomib treatment and a pulse of carfilzomib exposure than normal keratinocytes. (D) The proteolytic activities of the proteasome were assayed 8 hours after the addition of carfilzomib. The results were expressed as a percentage of the activity with carrier alone. Values are the mean -/+ the range of 2 independent experiments. Cell death in RDEB cSCC cell lines in response to continuous exposure to carfilzomib occurred at carfilzomib concentrations where only the chymotrypsin-like activity was inhibited. Death of cSCC cells induced by a short pulse of carfilzomib was associated with robust inhibition of the chymotrypsin-like activity and moderate inhibition of both the caspase and trypsin-like activities.