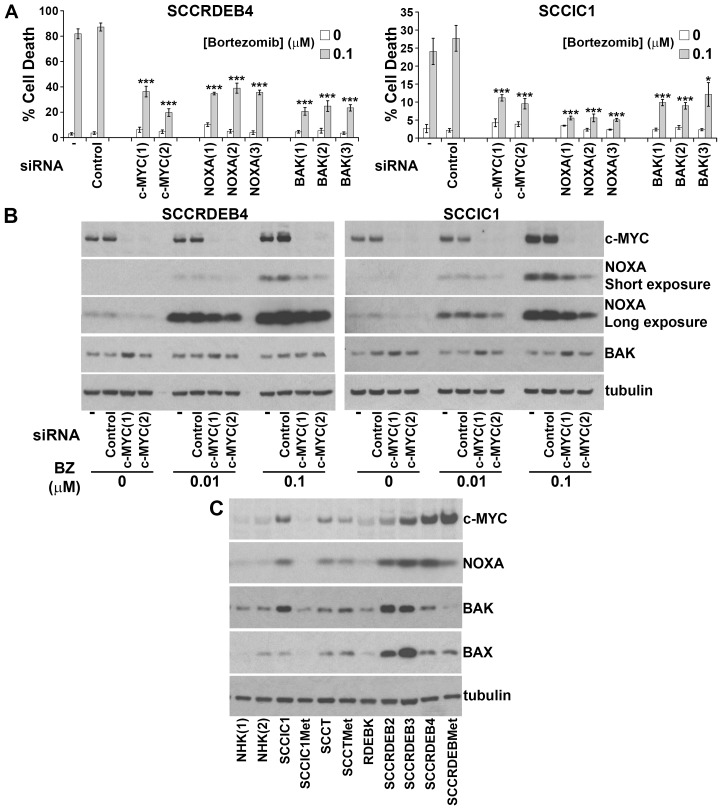
Figure 5. c-MYC-mediated NOXA upregulation is required for BAK-dependent cell death in response to a pulse of bortezomib.
(A) SCCRDEB4 and SCCIC1 cells, in which cell death is sensitive to a pulse of bortezomib, were mock-transfected (-) or transfected with a non-targeting siRNA (Control) or siRNAs targeting c-MYC, NOXA and BAK. siRNAs 1 to 3 are complementary to different sequences within the indicated target. Cells were exposed to an 8-hour pulse of bortezomib and cell death was assessed 24 hours after drug addition by real-time imaging. Values are the mean -/+ SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. Knockdown of c-MYC, NOXA, and BAK attenuated cell death in response to a short exposure to bortezomib (* P < 0.05 and *** P < 0.005 compared with control siRNA transfected cells). (B) SCCRDEB4 and SCCIC1 cells were mock-transfected (-) or transfected with non-targeting control siRNA or siRNAs complementary to c-MYC. Cells were treated with carrier or bortezomib (BZ) and were analysed by western blotting 8 hours after drug addition. A cytotoxic concentration of bortezomib (0.1μM) caused c-MYC-dependent accumulation of NOXA. (C) The expression of the indicated proteins was analysed by western blotting in the panel of cells used in this study. NHK (1) and (2) are from two different donors. Bortezomib-resistant normal keratinocytes and SCCIC1Met cells expressed low levels of c-MYC and NOXA while bortezomib-resistant SCCRDEBMet cells had low BAK levels.