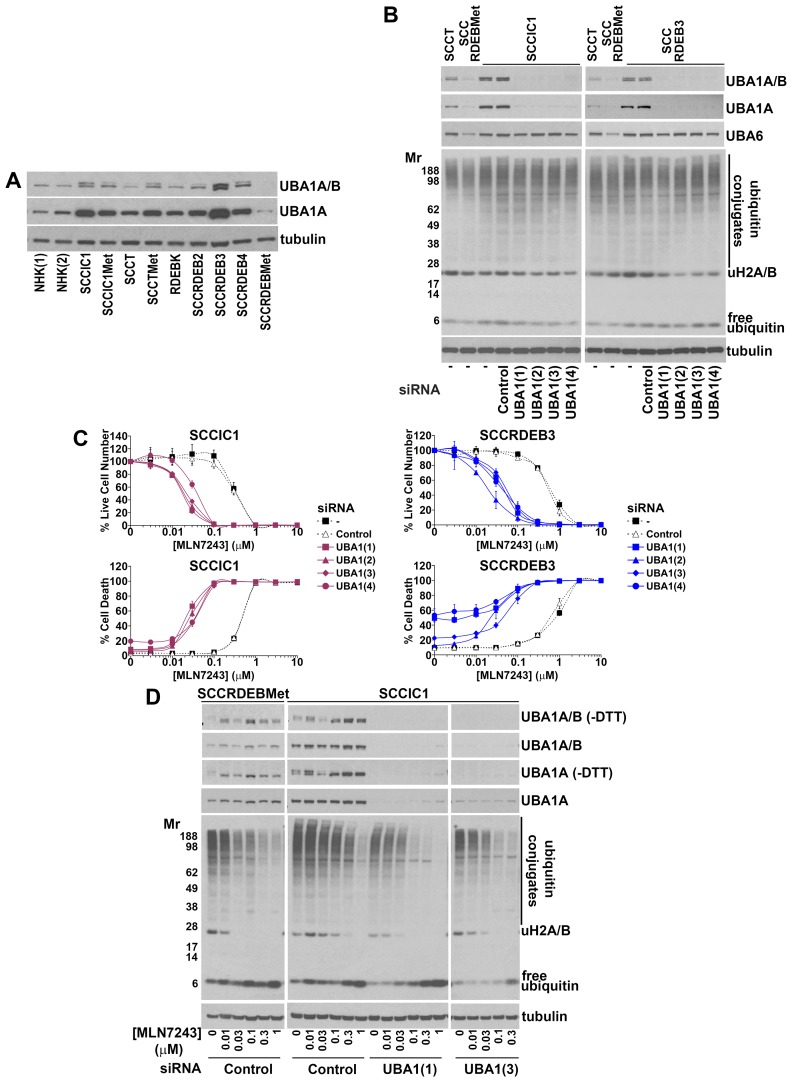
Figure 7. Low UBA1 protein expression is a determinant of sensitivity to MLN7243.
(A) The expression of UBA1 in the panel of cells used in this study was analysed by western blotting. This was carried out using a primary antibody that detects both major UBA1 isoforms: UBA1A (upper band) and UBA1B (lower band) and an antibody that is specific for UBA1A. UBA1A and B expression was lowest in MLN7243-sensitive SCCRDEBMet and SCCT cells while UBA1A expression was high in MLN7243-resistant SCCRDEB3 and SCCIC1 cells. (B) MLN7243-resistant SCCIC1 and SCCRDEB3 cells were mock-transfected (-) or transfected with the indicated siRNAs. UBA1 siRNAs 1 to 4 are complementary to different UBA1 sequences. Ubiquitin E1 expression and the pattern of ubiquitination were analysed by western blotting 72 hours after transfection. The UBA1 siRNAs efficiently depleted UBA1 while having no effect on the level of UBA6 or bulk high molecular weight ubiquitin conjugates. (C) MLN7243-resistant SCCIC1 and SCCRDEB3 cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting UBA1. Cell viability (live cell number) expressed as a percentage of carrier alone for each siRNA and cell death were analysed by real-time imaging 72 hours after the initiation of continuous incubation with MLN7243. Values are the mean -/+ SEM of 3 experiments. Knockdown of UBA1 dramatically increased sensitivity to MLN7243. (D) MLN7243-sensitive SCCRDEBMet cells and MLN7243-resistant SCCIC1 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. Samples were analysed by western blotting for UBA1 and ubiquitin 12 hours after initiating continuous incubation with MLN7243. More slowly migrating UBA1-ubiquitin thioesters were preserved by running samples in the absence of reducing agent (-DTT). MLN7243 decreased UBA1 thioesters. Cells with low UBA1 expression were more sensitive to MLN7243-induced decreases in high molecular weight ubiquitin conjugates and ubiquitinated histone H2A/H2B.