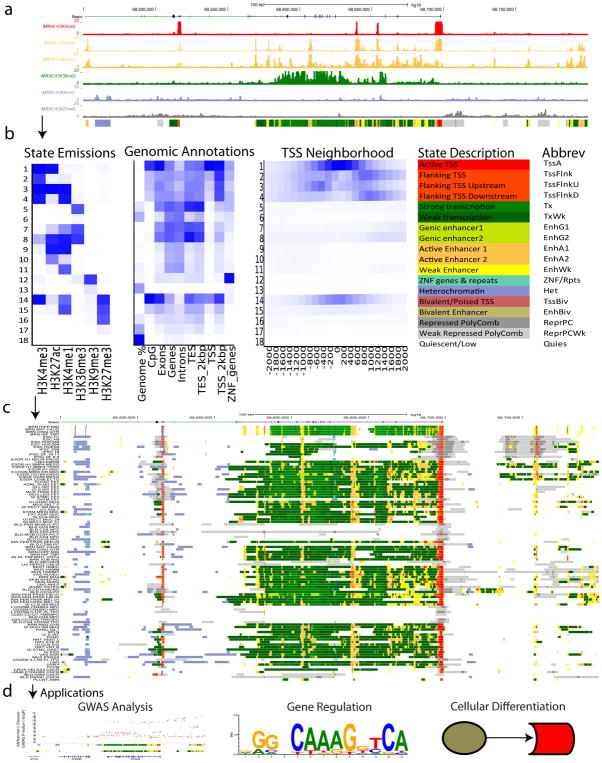
Figure 1. Overview of ChromHMM.
(a) Tracks of multiple histone modifications are shown from one cell type, IMR90. From such types of tracks, ChromHMM learns a set of chromatin state definitions de novo, and then assigns each location in the genome to an instance of each state. The chromatin states assignments for IMR90 based on the model in (b) are shown below the histone modifications. (b) The panel displays on left a heatmap of emission parameters where each row corresponds to a different state and each column a different mark for the Roadmap Epigenomics 18-state expanded model defined based on the observed data for six histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K9ac, H3K27ac, H3K36me3, and H3K9me3) from Ref. 3. The darker the blue color corresponds to a greater probability of observing the mark in the state. The heatmap to the right of the emission parameters displays the overlap enrichment for various external genomic annotations in IMR90 cells (epigenome E017) similar to what was previously shown for H1-hESC cells in Ref. 3. A darker blue color corresponds to a greater fold enrichment for a column specific coloring scale. The heatmap to the right of that shows fold enrichment for each state for each 200bp bin position within 2kb around a set of transcription start sites (TSS). A darker blue color corresponds to a greater fold enrichment and there is one color scale for the entire heatmap. Shown to the right of that are candidate state descriptions for each state followed by a state mnemonic. (c) The panel displays the browser view of ChromHMM genome annotation based on the model in (b), which was defined across 98 cell and tissue types3. Each row below the genes corresponds to one of the cell or tissue type. (d) The panel highlights application areas of ChromHMM, which include GWAS analysis, gene regulation, and cellular differentiation among others. The GWAS example shows overlap between chromatin state annotations and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) similar to Ref. 29. Roadmap epigenomics chromatin state annotations based on the model in (b) for primary monocytes cells (E029) and below it brain hippocampus (E071).