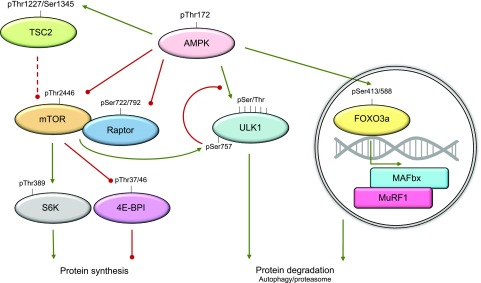
Figure 5.
Role of AMPK in protein metabolism. Activation of AMPK increases phosphorylation of regulatory associated protein mTOR (Raptor) and mTORC1 itself as well as TSC2, an indirect inhibitor of mTORC1. This decreases the activity of S6 kinase (S6K) and inhibits the release of binding partner eukaryotic translation factor 4E (eIF4E) from eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-BP1, thereby diminishing protein synthesis. Besides its effect on protein synthesis, AMPK promotes autophagy and proteasomal-mediated protein degradation by phosphorylating ULK1 (Ser317/467/555/637/777 and Thr575) and FOXO3a, respectively. When phosphorylated, FOXO3a increases the expression of E3 ligases MAFbx and MuRF1. Green lines, promotive; red lines, inhibitory; dashed line, indirect. Adapted from Sanchez et al. (42).