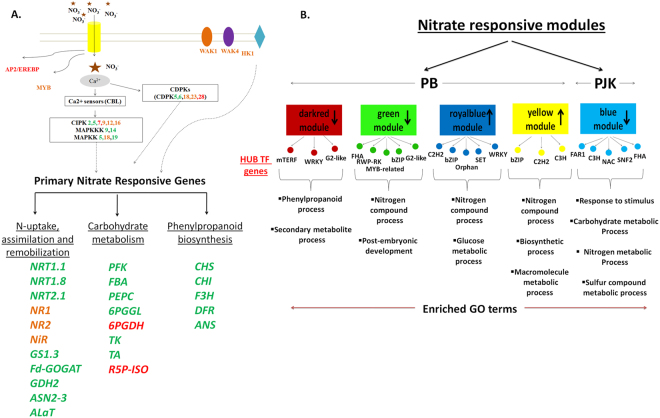
Figure 7.
Proposed model depicting nitrate responsive genes and nitrate regulated network in B. juncea cv. PB and PJK: Nitrate as a signal leads to activation of several signalling pathways which include transcription factors (MYB, AP2/EREBP) and protein kinases (WAK, HK, CIPK, CDPK) (A). These downstream regulatory component lead to the transcriptional regulation of several pathways involved in plant growth and development. The nitrate responsive genes induced early in high NUE cultivar, PB or low NUE, cultivar PJK or in both are represented by green, red and orange color, respectively (A). Co-expression network analysis revealed four significantly enriched nitrate regulated modules in PB and one in PJK (B). The enriched GO terms associated to each module are also shown. The black arrows inside the respective nitrate-regulated modules represent up or down regulation in response to nitrate treatment (B). WAK: wall associated kinases, CBL: Calcineurin B- like protein, CIPK: CBL-interacting protein kinases, CDPK: Ca2+ dependent protein kinases, MAPKKK: Mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase, MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase, NRT: Nitrate transporters, NR: Nitrate reductase, NiR: Nitrite reductase, GS: Glutamine synthetase, Fd-GOGAT: Glutamate synthase, GDH2: Glutamate dehydrogenase, ASN: Asparagine synthetase, ALaT: Alanine aminotransferase, PFK: Phosphofructokinase, FBA: Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, PEPC: Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, 6PGGL: 6-phosphogluconolactonase, 6PGDH: 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, R5P-ISO: Ribose 5-phosphate isomerase A, TK: Transketolase, TA: Transaldolase, CHS: Chalcone synthase, CHI: Chalcone-flavanone isomerase, F3H: Flavanone 3-hydroxylase, DFR: Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase, ANS: Anthocyanidin synthase.