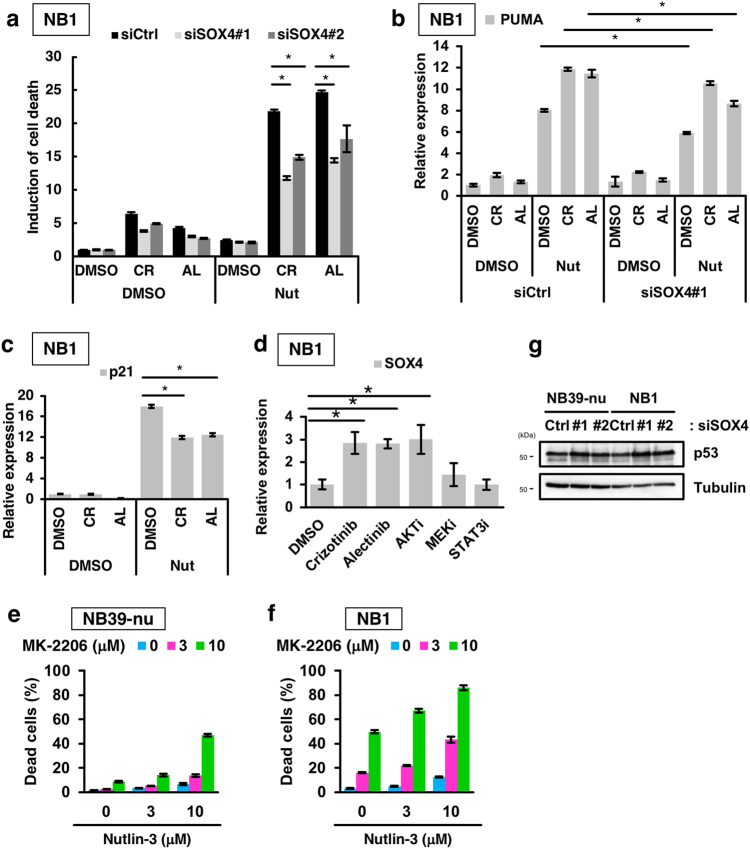
Fig. 7. SOX4 is involved in the regulation of p53-mediated target selectivity and induction of cell death elicited by combination treatment.
a Abrogation of cell death elicited by combination treatment following knockdown of SOX4. NB1 cells were transfected with either of the two SOX4 siRNAs, treated with 1000 nM ALK inhibitors, and 10 µM Nutlin-3 for 48 h, and a CytoTox GLO assay was carried out. b,c SOX4 is required for the specific induction of pro-apoptotic PUMA but not pro-cell cycle arrest p21. NB1 cells were transfected with a SOX4 siRNA and treated with 1000 nM ALK inhibitors and 10 µM Nutlin-3 for 16 h. The expression of PUMA and p21 were determined by qRT-PCR. See also Supplementary Figure 4e, 4f. d Regulation of SOX4 expression by the ALK–AKT axis. NB1 cells were treated with the indicated inhibitors (crizotinib, alectinib:1 µM, AKTi: 5 µM, MEKi: 1 µM, STAT3i: 75 µM) for 24 h. The expression of SOX4 was then measured by qRT-PCR. e,f Combination treatment of Nutlin-3 with the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in ALK-amplified neuroblastomas. NB39-nu cells (e) and NB1 cells (f) were treated with MK-2206 and Nutlin-3 as indicated for 48 h and a CytoTox GLO assay was performed. g The knockdown of SOX4 has no effect on the stability of p53 proteins. NB39-nu and NB1 cells were transfected with a SOX4 siRNA. After 48 h of transfection, an immunoblot analysis was carried out using the indicated antibodies. All data show the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05. All experiments were repeated at least three times