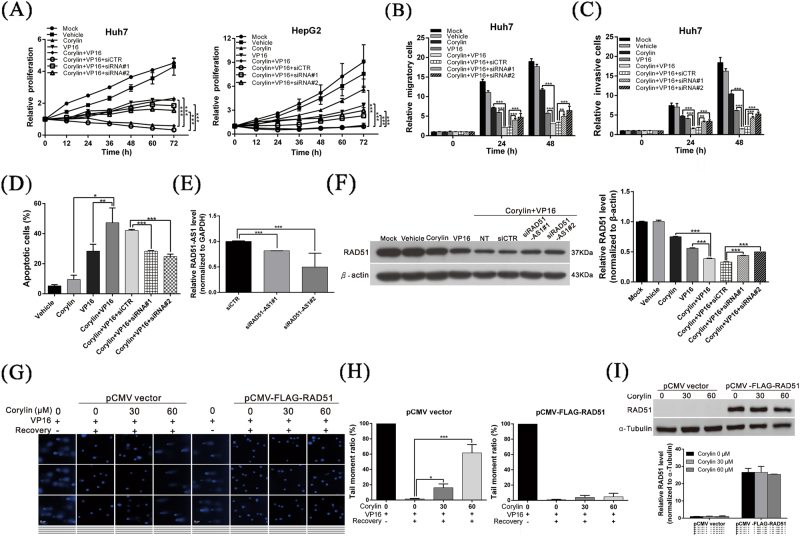
Fig. 5. Corylin increases the sensitivity of HCC cells to a chemotherapeutic agent by inducing lncRNA RAD51-AS1.
a–d The effects of corylin (30 μM) combined with etoposide (VP16) (200 μM) on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis with/without treatment with RAD51-AS1 siRNA (50 nM) in HCC cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, as assessed using the Student’s t-test. e Real-time PCR analysis shows the mRNA levels of RAD51-AS1 during the siRNA treatments. f Western blot analysis shows the effect of the above treatments on the expression of RAD51 (left panel). The quantitative results are shown in the right panel. ***p < 0.001. g Comet assays show that the overexpression of the RAD51 protein attenuates the inhibition of DNA repair by corylin. The quantitative cell repair activity results are shown in h. All data were expressed as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. i Western blot analysis shows the effect of the above treatments on the expression of RAD51 (upper panel). The quantitative results are shown in the lower panel. ***p < 0.001