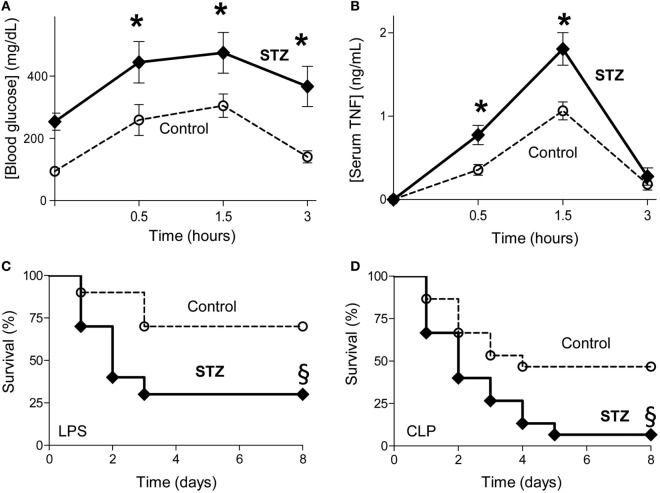
Figure 1.
Diabetes worsening systemic inflammation and survival in sepsis. (A,B) Control (non-diabetic treated with vehicle solution) or diabetic [STZ; 40 mg/kg] mice were challenged with LPS (10 mg/kg; i.p., n = 4; *p < 0.05 vs. control, two-way ANOVA). (A) Blood glucose or (B) serum tumor necrosis factor (TNF) levels were analyzed at the indicated time points post LPS. (C,D) Kaplan–Meier survival analyses of control or diabetic (STZ) mice challenged with (C) endotoxemia (LPS, 10 mg/kg; i.p.; n = 10) or (D) polymicrobial peritonitis induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP; n = 15). §p < 0.05 vs. control, survival log-rank test.