Figure 1.
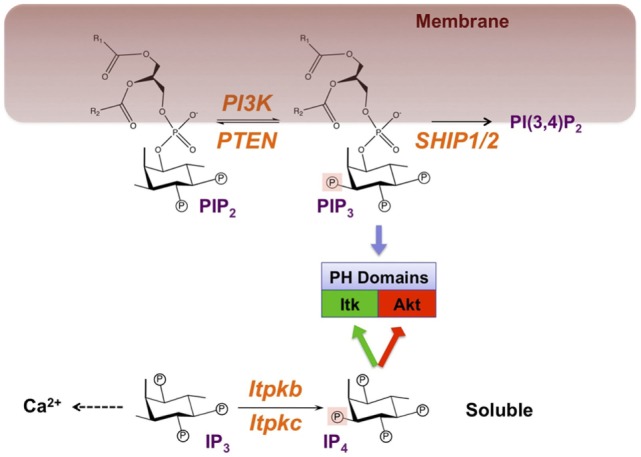
Symmetric signaling by phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K) and Itpkb controls effector recruitment through the analogous but phase-separated pleckstrin homology (PH) domain ligands PIP3 and IP4. Engagement of antigen receptors activates PI3K, which phosphorylates the membrane-lipid phosphatidylinositol(4,5) bisphosphate (PIP2) on the 3-position of its cytoplasm-exposed inositol ring to generate phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5) trisphosphate (PIP3). Alternatively but not shown to emphasize the PI3K/Itpkb symmetry, phospholipase-Cγ1 (PLCγ1) can hydrolyze PIP2 into the second messengers diacylglycerol (DAG) and soluble inositol(1,4,5) trisphosphate (IP3). Canonically, PIP3 accumulation is limited through its removal by two families of phospholipid phosphatases: Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) which reverses the PI3K reaction, and SH2 domain-containing inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatases (SHIP-1/2) which convert PIP3 into phospatidylinositol(3,4) bisphosphate [PI(3,4)P2]. Mainly through their IP headgroups, PIP2, PIP3, and PI(3,4)P2 can bind to PH and other domains in signaling proteins such as Itk and Akt, and recruit them to membranes. IP3 mobilizes Ca2+ but can also be phosphorylated at its 3-position into Inositol(1,3,4,5) tetrakisphosphate (IP4) by IP3 3-kinases (Itpka/b/c and inositol-phosphate-multikinase) (8, 19). Because it resembles the PIP3 headgroup, IP4 can also bind to certain PIP3-binding PH and other domains and promote (green) or inhibit (red) PIP3 binding. In CD4+CD8+ thymocytes, IP4 promotes PIP3 binding to the Itk/Tec PH domains to establish a feedback loop of PLCγ1 activation (20, 21). In neutrophils, NK cells, CD4−CD8− thymocytes undergoing β-selection and in hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), IP4 competition with PIP3 or PI(3,4)P2 for binding to its PH domain may limit Akt membrane recruitment and activation (22–27). IP4 can also inhibit RASA3/GAP1IP4BP-binding to PI(4,5)P2 or PIP3 (28, 29). Whether this occurs in immunocytes remains unknown. R1, R2, fatty acid side-chains. Circled P, phosphate moiety. Orange, enzymes with demonstrated physiological relevance in immunocytes.
