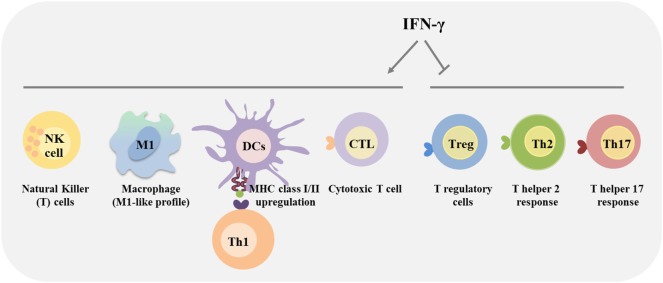
Figure 2.
Immunomodulatory effects of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). IFN-γ produced by immune cells affects the behavior of distinct immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. Specifically, IFN-γ plays a major role in activating anticancer immunity, by promoting the activity of CD4 T helper type 1 cells, CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL), natural killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells (DCs), and macrophages, promoting the antigen presentation. Additionally, IFN-γ activates macrophages towards a more pro-inflammatory and tumoricidal phenotype (M1-like). Alternatively, IFN-γ inhibits regulatory T (Treg) cells, Th2 and Th17 differentiation and functions.