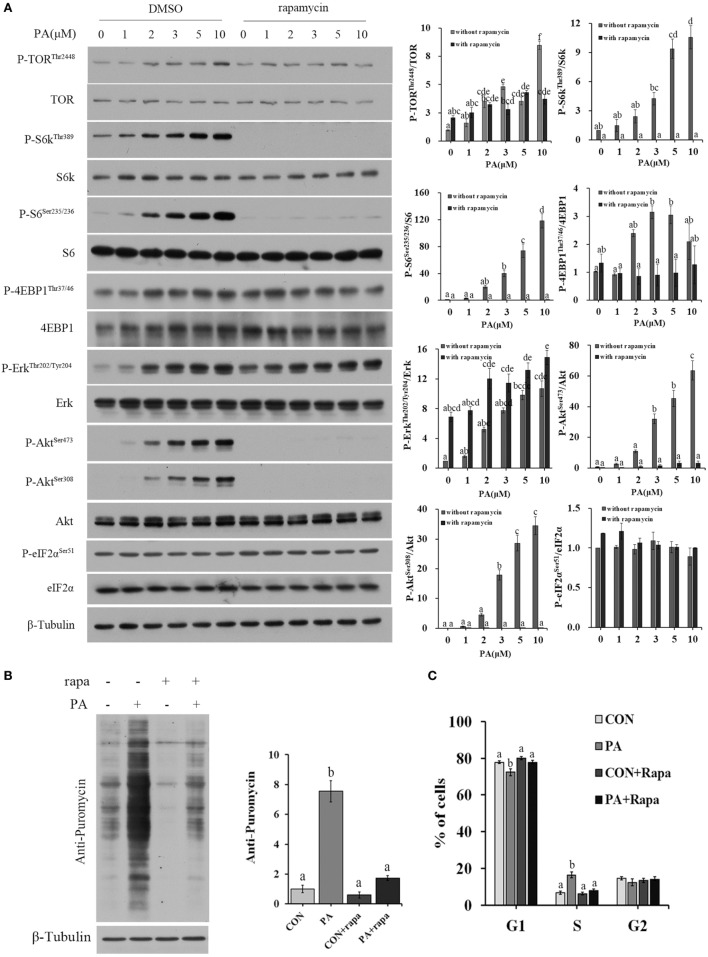
Figure 4.
Phosphatidic acid (PA) induced cellular protein synthesis and G1/S phase transition in a target of rapamycin (TOR)-dependent manner. Serum starved cells were treated with indicated concentrations of PA with or without rapamycin for 16 h. (A) The levels of total and phosphorylated forms of TOR, S6k, S6, 4EBP1, Erk, Akt, and eIF2α were examined by western blot after treatment and quantitated (n = 3). (B) Cellular protein synthesis was analyzed by western blot using SUnSET technique after treatment (n = 3) and quantitated. (C) Cell cycle distribution was analyzed using flow cytometry with PI staining after treatment and quantitated (n = 3). Results were represented as means with SEs and significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range tests. a,b,c,d,e,f means with different letters were significantly different, P < 0.05.