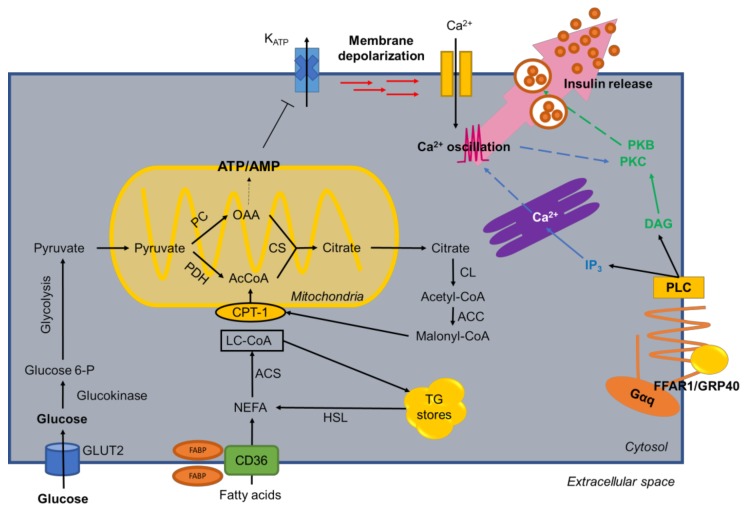
Figure 2.
General metabolism of fatty acids in β-cells. The main metabolic pathways of FFAs are outlined in the figure, such as glycolysis, FA biosynthesis, β-oxidation. Glycolysis produces an increase in ATP, which closes K(ATP)-dependent channels and causes membrane depolarization and the opening of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels, stimulating insulin release. Also, the binding of fatty acids to free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFAR1) generates changes of Ca2+ in ER lumen promoting insulin release in β-cell.