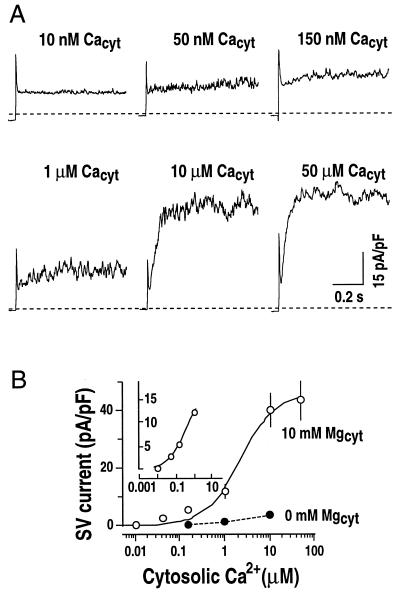
Figure 5.
Cytosolic Mg2+ sensitizes SV channels to cytosolic Ca2+. A, Representative whole-vacuole currents recorded at different cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations in two separate vacuoles. In one vacuole, cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations were changed from 10 nm to 1 μm by either local or bath perfusion (vacuolar capacitance = 3.5 pF). In another vacuole, 10 μm Ca2+ in the bath solution was replaced by 50 μm Ca2+ (vacuolar capacitance = 4.2 pF). Only current traces at +100 mV are shown. Dashed lines show zero current levels. Pipette solution contained 20 mm KCl, 2 mm EGTA, and 5 mm HEPES-Tris, pH 7. Bath solution contained 200 mm KCl, 10 mm MgCl2, and 20 mm HEPES-Tris, pH 8.0, with varying free Ca2+ concentrations of 0, 10 nm, 50 nm, 150 nm, 1 μm, 10 μm, and 50 μm (see “Materials and Methods” for details). B, Effect of cytosolic Mg2+ on cytosolic Ca2+ activation of SV currents at +100 mV as performed in A. In control experiments, SV currents were recorded at 0 mm Mg2+ in bath solutions (●). Values are from three to eight vacuoles (capacitance = 4.7 ± 1.2 pF). A Hill curve is fitted to the data for the SV currents activated by Ca2+ at 10 mm cytosolic Mg2+. Data obtained at 10 nm to 1 μm cytosolic Ca2+ are shown in the inset (Kd approximately 227 nm).