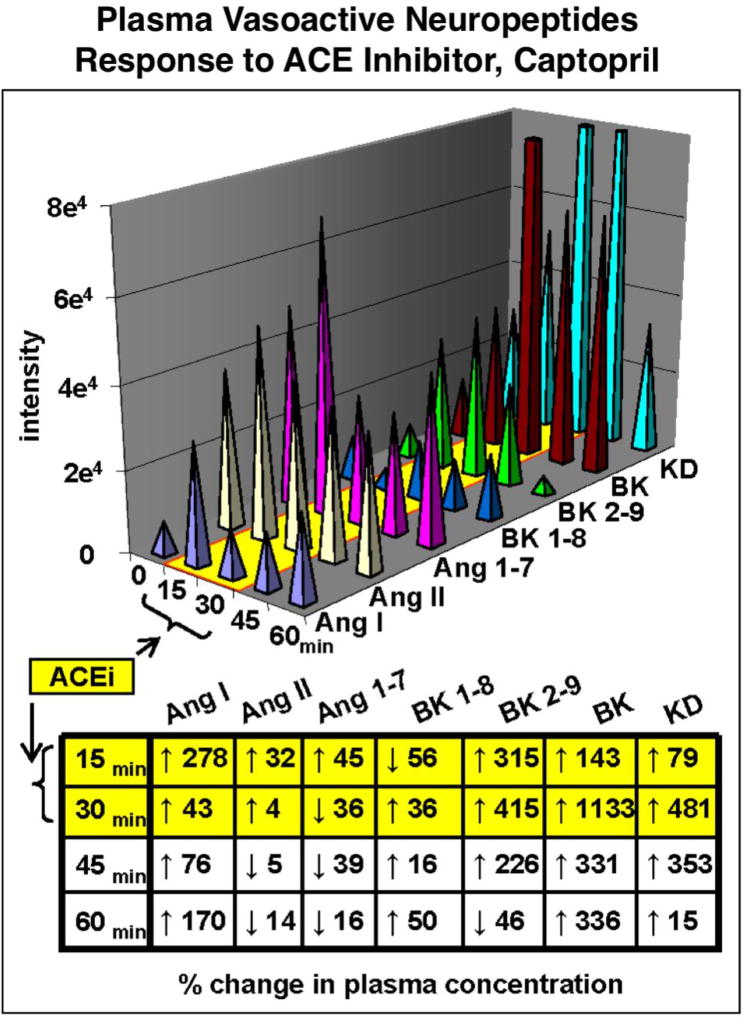
Figure 6. Regulation of vasoactive neuropeptide profiles by captopril inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE).
Plasma neuropeptides in rat were analyzed by neuropeptidomics after administration of captopril, an anti-hypertensive drug inhibitor of the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). Neuropeptidomics was assessed in time-course studies by nano-LC-MS/MS with quantitation using stable isotope-labeled internal standards [9]. Separation of peptides by chromatography and multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) quantitated angiotensin I (Ang I), Ang II, Ang1–7, bradykinin 1–8 (BK 1–8), BK-2–9, and kallidin (KD) vasoactive neuropeptides involved in blood pressure regulation. The angiotensin peptides were significantly reduced by the ACE inhibitor, with parallel increases in bradykinins and kallidin (potent vasodilator). The percent change in plasma concentration at each time point after drug administration is shown. These results demonstrate simultaneous profiling of multiple plasma peptides by neuropeptidomics to assess drug-induced changes in vasoactive neuropeptides.