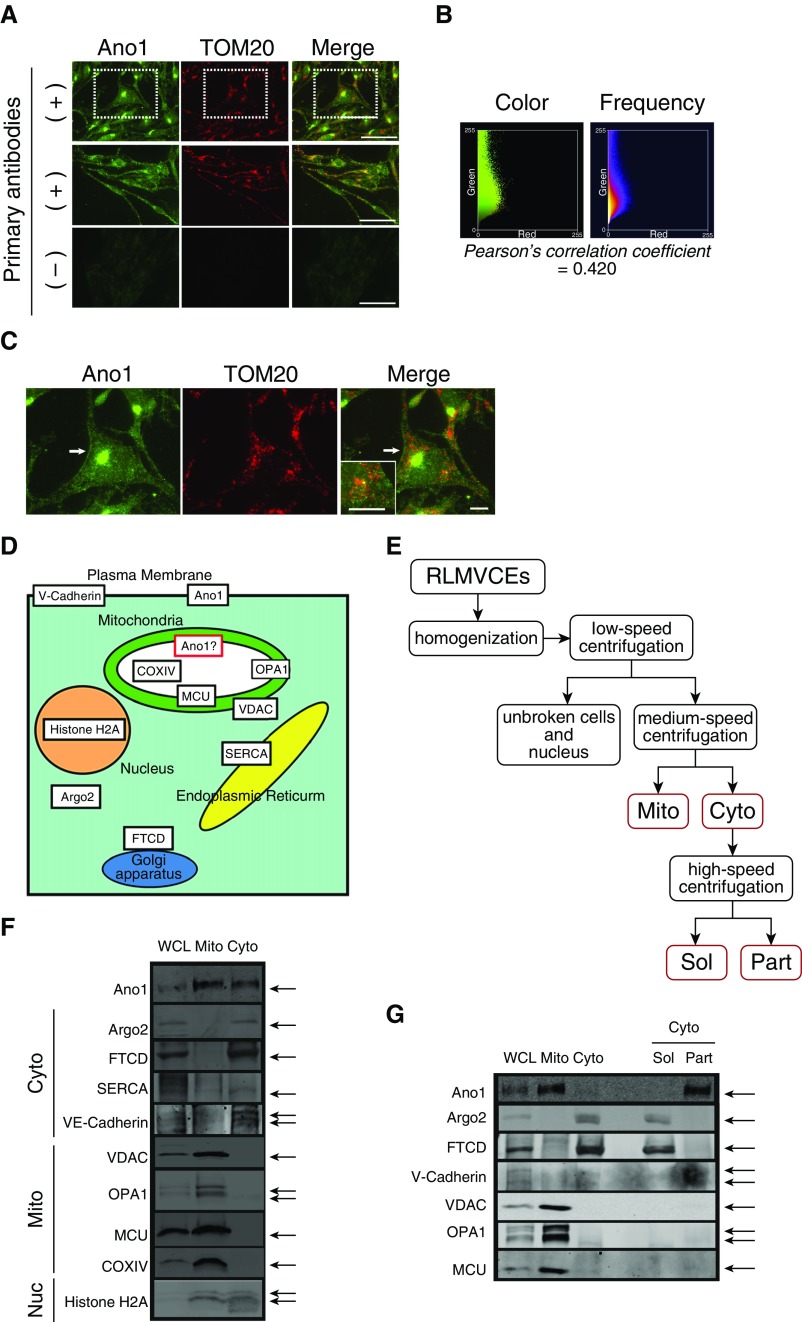
Figure 1.
Subcellular localization of anoctamin (Ano)-1 in primary pulmonary endothelial cells (ECs). (A) Immunofluorescence images of rat lung microvascular ECs (RLMVECs) labeled with Ano1 (green) and the mitochondrial marker translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane 20 (TOM20; red) antibodies (top and middle panels). Control experiments were performed using secondary antibodies without primary antibodies, which showed no noticeable labeling (bottom panels). Higher magnification of dotted square regions is shown in C. Scale bars = 50 μm. (B) Frequency and color scatter plots generated from top panel images in A. Pearson’s correlation coefficient value calculated from A indicates partial colocalization of Ano1 and TOM20. (C) Higher magnification of RLMVEC image from A. Ano1 is localized to the plasma membrane (white arrow) and intracellular compartments, including mitochondria (inset). See also Figure E1 and Video E1. Scale bars = 10 μm. (D) Schematic diagram of selected marker proteins and potential subcellular Ano1 localization. (E) Schematic steps of mitochondria isolation. Cyto = cytosolic fraction including other non-mitochondrial membrane structures (e.g., endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus, and Golgi apparatus) and plasma membrane; Mito = mitochondrial-enriched raction; Part = insoluble (particle) proteins obtained from the Cyto fraction by ultracentrifugation; Sol = soluble fraction, obtained from the Cyto fraction by ultracentrifugation. (F) Representative immunoblot of whole-cell lysate (WCL), Mito fraction, and Cyto fraction from RLMVECs. To assess the purity of the Mito fraction after proteins were also blotted in addition to Ano1 (see also E): argonaute (Argo) 2 (cytosolic and ribosome-associated protein); Golgi 58K protein/formimino-transferase cyclodeaminase (FTCD; an enzyme associated with the cytoplasmic surface of the Golgi apparatus); sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA; sarco/endoplasmic reticulum protein); VE-cadherin (plasma membrane protein); and histone H2A (nucleus protein). Voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC; outer mitochondrial membrane protein); OPA1 (a protein located at the intermembrane space and inner mitochondrial membrane [IMM]), mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU; IMM protein) and COX IV (mitochondrial-matrix protein) were used as markers for the Mito fraction and for confirming the maintenance of mitochondrial structure integrity during the protein fractionation. Equal protein amounts of WCL, Cyto, and Mito fractions (30 μg/well) were separated by SDS-PAGE. (G) Representative immunoblot of Sol and insoluble Part (insoluble) proteins obtained from the Cyto fraction by ultracentrifugation (20 μg/well; see E and Methods in the data supplement). WCL, the Mito fraction, and the Cyto fraction (30 μg/well) were also blotted for comparison.