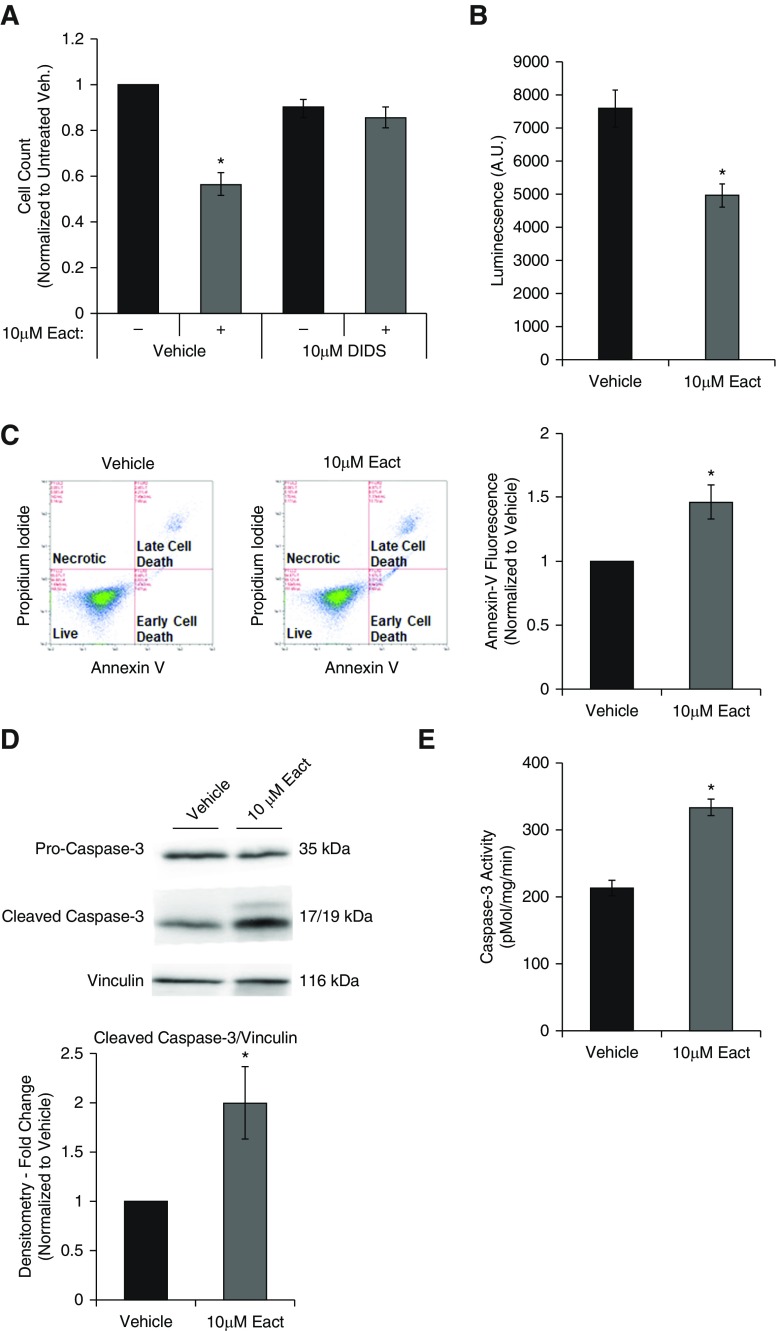
Figure 2.
Activation of Ano1 induces apoptosis in RLMVECs. RLMVECs were seeded subconfluently and allowed to adhere for 24 hours before quiescing for 24 hours. Cells were then treated with drugs as indicated for 24 hours in complete media. (A) Cells were treated with vehicle or 10 μM Eact for 24 hours in presence or absence of chloride channel inhibitor (10 μM 4,4′-diisothiocyano-2,2′-stilbenedisulfonic acid [DIDS]; n = 4, two-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison, *P < 0.05 vs. untreated control). (B) Cells were treated with vehicle or 10 μM Eact for 24 hours and cell viability was determined by luminescence viability assay (CellTiter-Glo; n = 5, *P < 0.05). (C) Cells were treated with vehicle or 10 μM Eact for 24 hours and stained for annexin-V and with propidium iodide and assessed using flow cytometry. The left two panels show representative dot plots of cells with different intensity of annexin-V and propidium iodide fluorescence. The right panel shows percent of cells positive for annexin-V fluorescence normalized to vehicle (n = 6, *P < 0.05). (D) Immunoblot of cleaved caspase-3 from RLMVECs treated with vehicle or 10 μM Eact for 24 hours (n = 5, *P < 0.05). (E) Caspase-3 activity from RLMVECs treated with vehicle or 10 μM Eact was measured using N-Acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin fluorogenic assay (n = 5, *P < 0.05). Data are presented as mean (±SEM). A.U. = arbitrary units; veh. = vehicle.