Fig. 5.
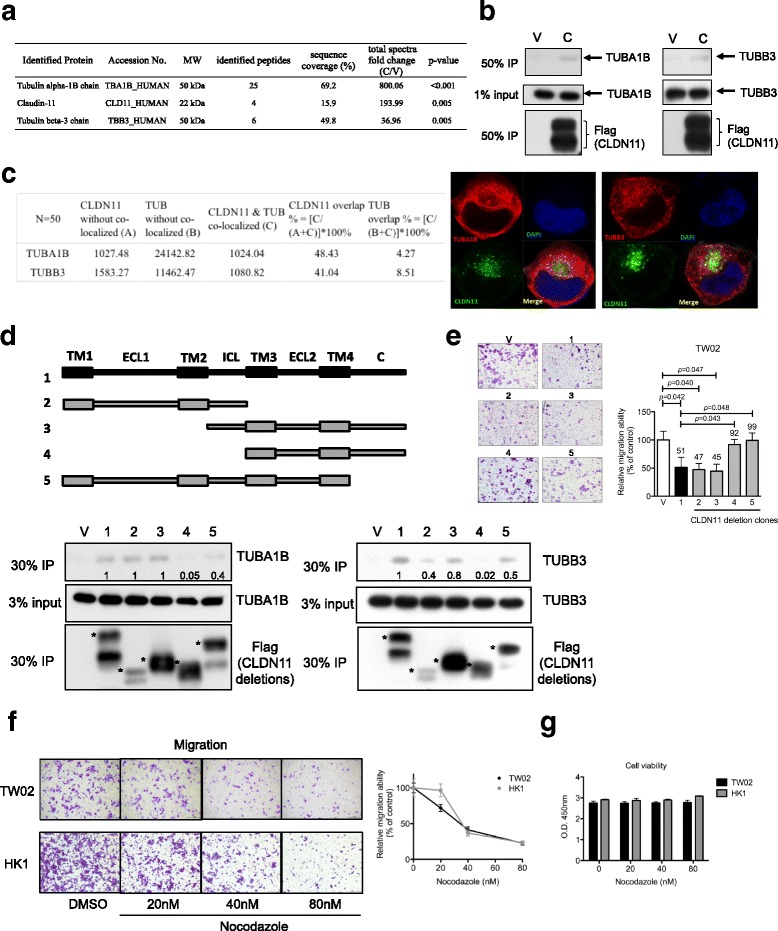
TUBA1B and TUBB3 are the interacting proteins of CLDN11; CLDN11 blocks cell migration by interfering with tubulin polymerization. a TW02 cells transfected with FLAG-tagged CLDN11 construct (C) or vector control plasmid (V) were harvested after 48 h. TW02 cell extracts and M2 beads were used for a co-immunoprecipitation assay. CLDN11-interacting proteins identified through LC–MS/MS and top-ranking proteins are listed in the table. b Immunoblot analyses were performed to confirm the interaction between FLAG-tagged CLDN11 and endogenous TUBA1B (left panel) or TUBB3 (right panel). c Subcellular distribution of exogenous FLAG-tagged CLDN11 and endogenous TUBA1B or TUBB3 in TW02 cells was assayed through immunofluorescence staining 24 h after transfection. The fluorescent signal (pixel) of each individual cell was quantitated by using the Zen 2.0 software (n = 50). The proportion of colocalized fluorescent signals (%) is indicated (FLAG-tagged CLDN11, green; Tubulins, red; DAPI, blue). d Schematic illustrations of WT and four deletion FLAG-tagged CLDN11 molecules—transmembrane (TM), extracellular loop (ECL), intracellular loop (ICL), and C-terminus (C). Various FLAG-tagged CLDN11 deletion clones or a vector control were used to dissect the interacting domains on CLDN11 that are crucial for the interaction of endogenous TUBA1B and TUBB3. Input (3%) and immunoprecipitates (30% IP) were assayed through immunoblot analysis by using appropriate antibodies (anti-Flag, anti-TUBA1B and anti-TUBB3). The asterisks denote the major bands of ectopic CLDN11 in the immunoblot assays. e CLDN11 deletion clones were used to perform cell migration assay and to determine which domains on CLDN11 are necessary for blocking cell migration in TW02 cells. f Cell migration and (g) cell viability assays were performed in the presence or absence of nocodazole in TW02 or HK1 cells
