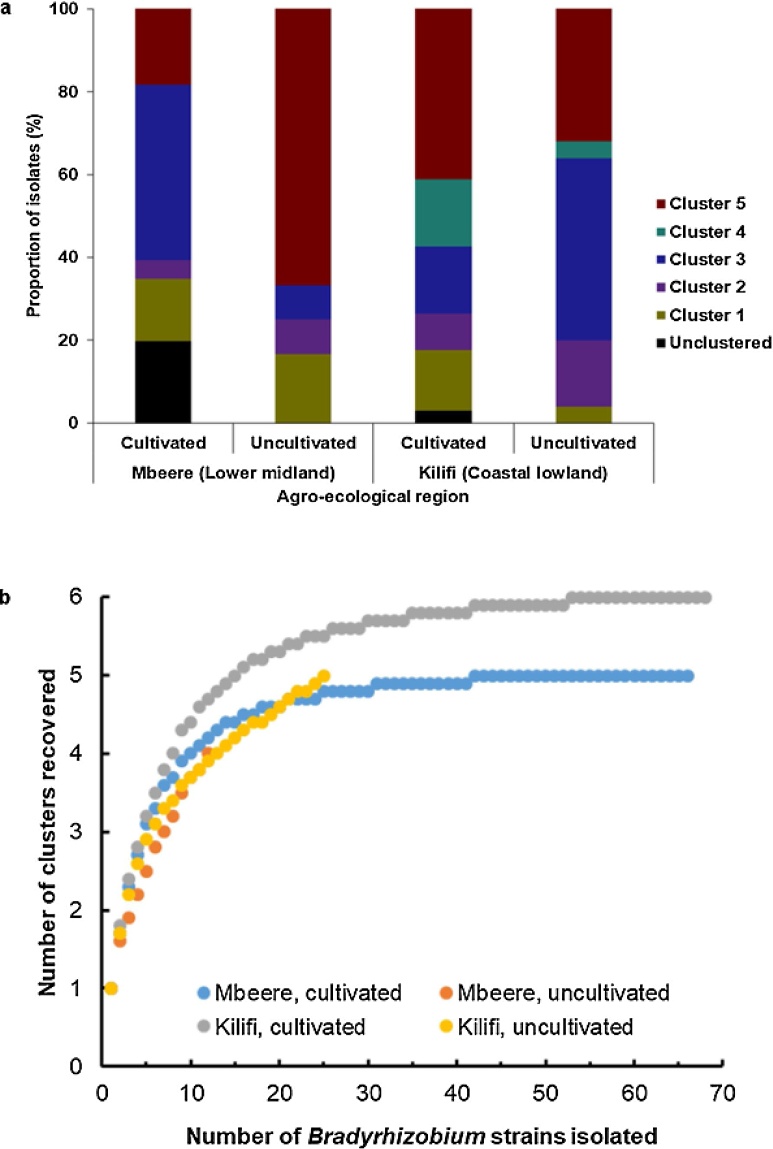
Fig. 3.
(a) Frequency of occurrence of five Bradyrhizobium isolate groups from root nodules of cowpea at cultivated and uncultivated sites in the agro-ecological regions around Mbeere and Kilifi in Kenya. The isolate grouping is based on similarity clustering of mass spectral protein profiles as determined by Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/ Ionization Time of Flight (MALDI-TOF) Mass Spectrometry (MS) (Fig. 1). Sampling took place at 15 cultivated and 5 uncultivated sites in each agro-ecological region. (b) Rarefaction curves of the number of different groups of Bradyrhizobium in the two agro-ecological regions and cultivated and uncultivated sites (Fig. 1). Number of isolates considered: Mbeere, cultivated: 66, uncultivated: 12; Kilifi, cultivated: 68, uncultivated: 25.