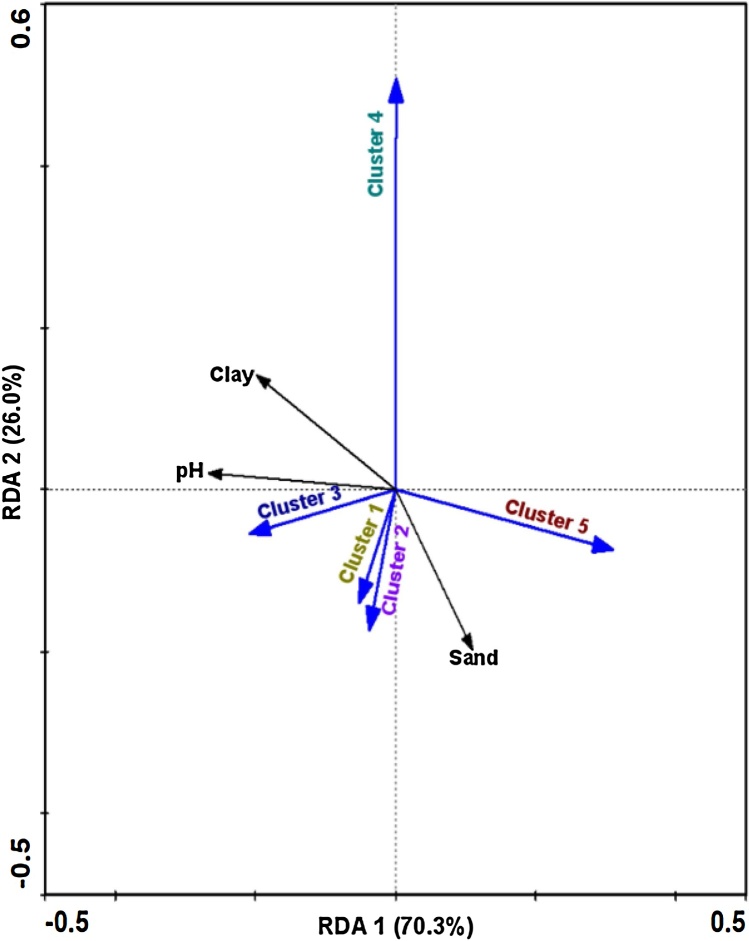
Fig. 4.
Correlative relationship between the occurrence of five similarity clusters of Bradyrhizobium root nodule isolates of cowpea and edaphic parameters as inferred by redundancy analysis (RDA). The biplot explains 96.3% of total variance in the dataset and is based on the presence/absence data of five similarity clusters of 156 Bradyrhizobium isolates, recovered from root nodules of cowpea plants growing in soil of 36 field sites. The vector sizes denote the strength of correlation and small angles indicate high correlation between environmental factors and/or cluster occurrence. Black arrows denote soil parameters, and blue arrows the Bradyrhizobium clusters, as characterized by similarity of MALDI-TOF MS protein mass spectra (Fig. 1, Fig. 3a). Percentages on the axes show the fraction of total variance explained. Only environmental parameters significantly correlated to the occurrence of the Bradyrhizobium clusters are shown. The pH (P < 0.05***), sand (P < 0.01**), and clay (P < 0.001*) concentrations, were those factors, which influenced Bradyrhizobium occurrence and symbiotic abundance. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)