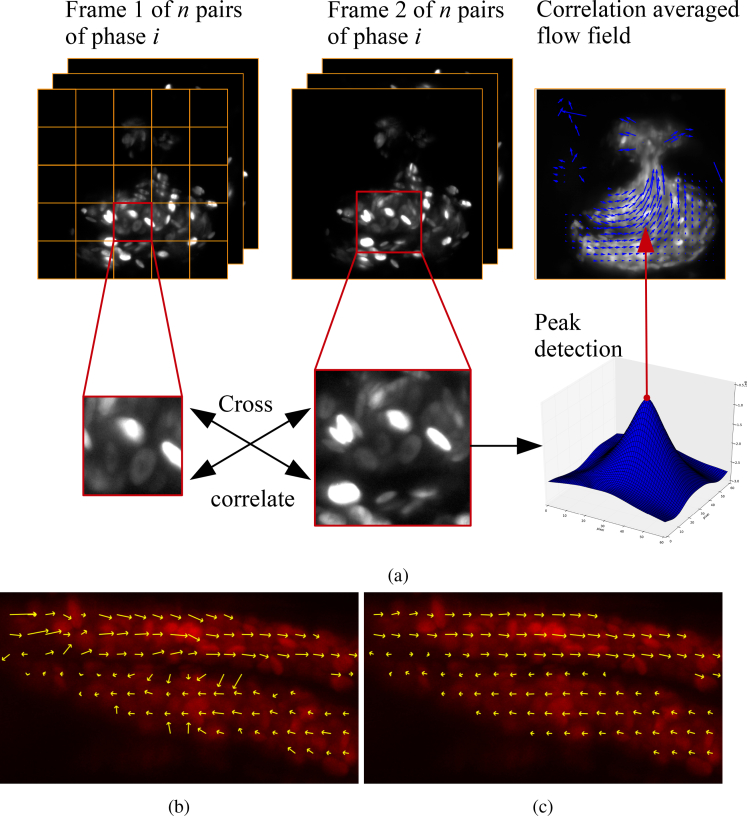
Fig. 2.
The PIV algorithm, and comparison between two shift estimation methods. (a) Sub-regions of the frame pairs are cross-correlated in time, yielding a matrix of the cross-correlation result, the peak of which then indicates the most likely motion of particle image between the two frames. Peak detection is then followed by subpixel interpolation of the peak and certain criteria tests probing the validity of the measurement, details in [25]. In case of correlation-averaging, each result IW pair matching from the same phase is averaged before peak fitting is executed. (b) shows the standard analysis based on direct cross correlation, while (c) illustrates our substitution of the sum of absolute differences metric in the cross-correlation stage of the analysis. Notice that the calculated flow in (b) is biased towards high intensities and produces vectors which appear to be pointing inwards, towards the center of the blood vessel. The same parameters were used in the PIV algorithm for both analyses.