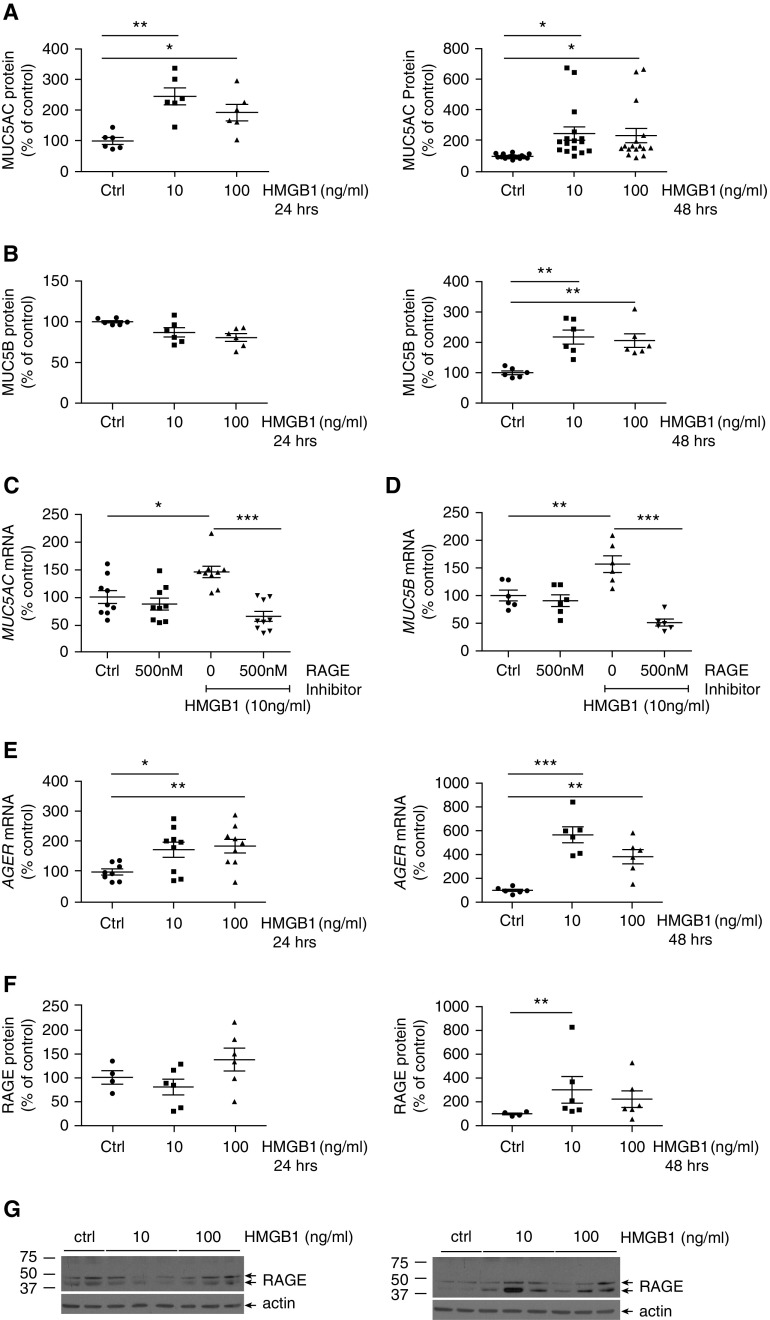
Figure 1.
High-mobility group box1 (HMGB1) upregulated MUC5AC and MUC5B protein expression, and gene regulation was blocked by a receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) inhibitor. Normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells were cultured at the air–liquid interface, treated with HMGB1 (10 or 100 ng/ml) for 24 or 48 hours, and analyzed for relative MUC5AC (A) and MUC5B (B) protein levels in the apical media by microtiter plate assay (see the data supplement). Involvement of the RAGE receptor in HMGB1-induced MUC5AC (C) and MUC5B (D) mRNA expression was tested by pretreatment with a RAGE inhibitor, FPS-ZMI (500 nM), for 1 hour, followed by administration of HMGB1 (10 ng/ml, 24 h). Expression of MUC5AC and MUC5B mRNA was determined by qRT-PCR as described in the data supplement. HMGB1 (10 or 100 ng/ml; 24–48 h) increased AGER (RAGE) mRNA expression (E) and RAGE protein levels as shown by densitometric analysis (F) of Western blots in well-differentiated, primary NHBE cells. A representative Western blot for RAGE is shown in G. RAGE mRNA was determined by qRT-PCR, and RAGE protein levels were compared with vehicle control–treated cells by Western blot, as described in the data supplement. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 comparisons between conditions are marked by lines). Two to five independent experiments with six or more replicates per experimental treatment condition were performed using NHBE cells obtained from two to five different donors. Ctrl = control.