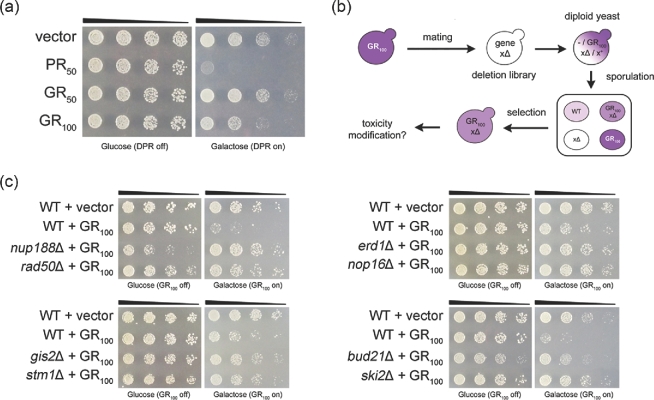
Figure 1.
A yeast deletion screen reveals genetic suppressors of GR100 toxicity. (A) GR toxicity is length-dependent and less severe than PR toxicity in yeast. Five-fold serial dilutions of yeast cells were spotted onto glucose- or galactose-containing plates. Galactose induced expression of GR or PR in yeast, while glucose repressed DPR expression. (B) Schematic of the yeast deletion screen. (C) Example spotting assays validating specific hits from the deletion screen. Expression of GR is no longer toxic in strains lacking Nup188 (nuclear pore protein), Rad50 (double stranded break repair protein), Erd1 (ER protein), Nop16 (nucleolar protein), Gis2 (translational activator of specific mRNAs), Stm1 (ribosome preservation factor), Bud21 (ribosomal biogenesis protein) or Ski2 (RNA helicase).