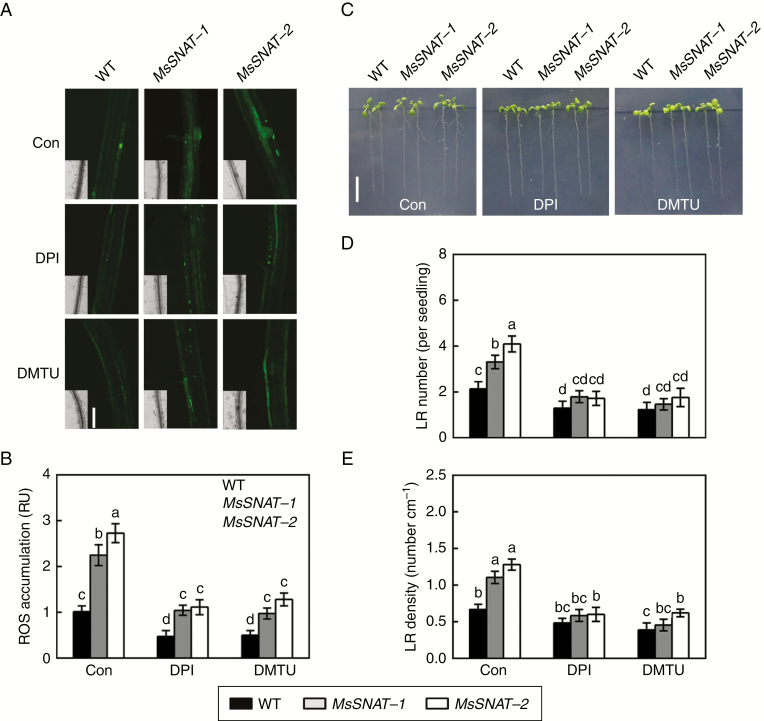
Fig. 5.
Genetic evidence showed that endogenous melatonin-induced ROS generation and thereafter lateral root formation are sensitive to DPI and DMTU. The SNAT gene of Medicago sativa (MsSNAT), encoding serotonin N-acetyltransferase, is homologous to the AtSNAT gene. Transgenic Arabidopsis lines overexpressing MsSNAT driven by the cauliflower mosaic virus were generated, and showed higher levels of endogenous melatonin (Gu et al., 2017). Four-day-old wild-type (WT) and transgenic seedlings (MsSNAT-1 and MsSNAT-2) were treated with or without 0.1 μm DPI or 0.1 mm DMTU. (A, B) After treatment for 36 h, root tissues were loaded with 20 μm H2DCFDA and regions of root mature zone were detected by LSCM. Fluorescence is shown as relative units (RU) of pixel intensity with reference to wild-type (Con). Scale bar (A) = 100 μm. Six individual plants were randomly selected and measured for each genotype per treatment. (C) Lateral root (LR) phenotypes after treatment for 5 d. Scale bar (C) = 1 cm. (D) Number of emerged LRs (>1 mm) per seedling. (E) Density of emerged LRs. Means and standard errors were calculated from at least three independent experiments with at least three replicates for each. Bars with different letters (B, D, E) denote significant differences (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test, P < 0 .05).