Figure 2.
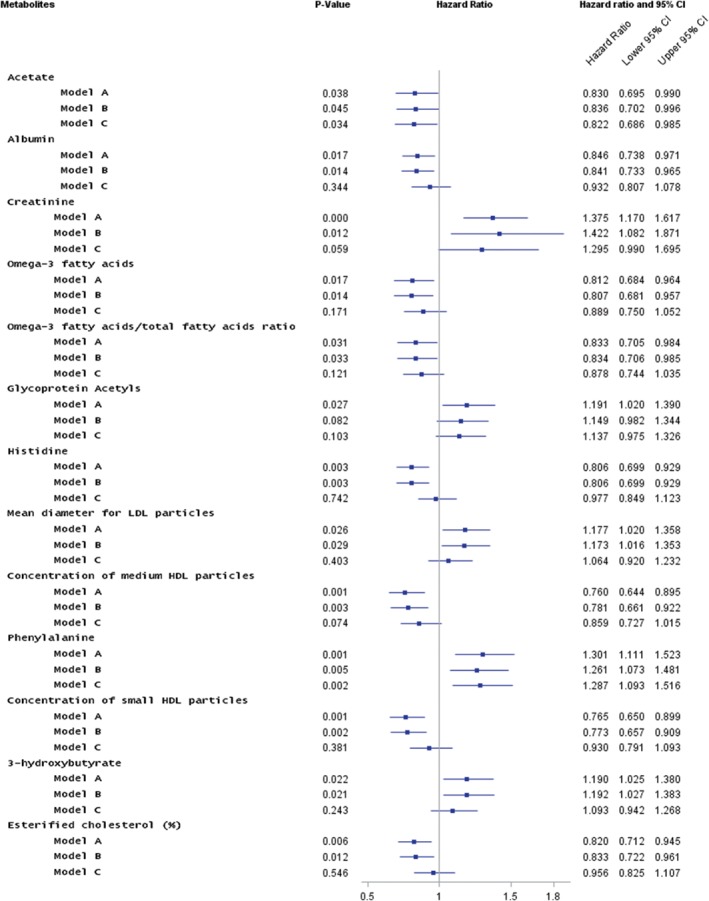
Forest plot of hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CI) of association for metabolites with incident heart failure hospitalisation (HFH) in PROSPER during 2.7 years of follow‐up. Associations were adjusted for treatment group, age, sex, smoking status, country, body mass index (BMI), myocardial infarction, systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP), coronary artery bypass graft, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, transient ischaemic attack, stroke, angina, claudication, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), N‐terminal pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide (NT‐proBNP) concentration (6‐month) and treatment with angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors, beta‐blockers, calcium channel blockers, anti‐arrhythmics and diuretics (note all medications are as recorded at baseline, 0 month). Nuclear magnetic resonance measures with P < 0.05 in Model A are shown. HDL, high‐density lipoprotein; LDL, low‐density lipoprotein. Model A: adjusted for sex, BMI, SBP, DBP, current smoking, diabetes, pravastatin/placebo, blood pressure‐lowering therapy, major coronary events/baseline cardiovascular disease. Model B: adjusted as for Model A plus eGFR. Model C: adjusted as for Model B plus NT‐proBNP.
