Figure 7.
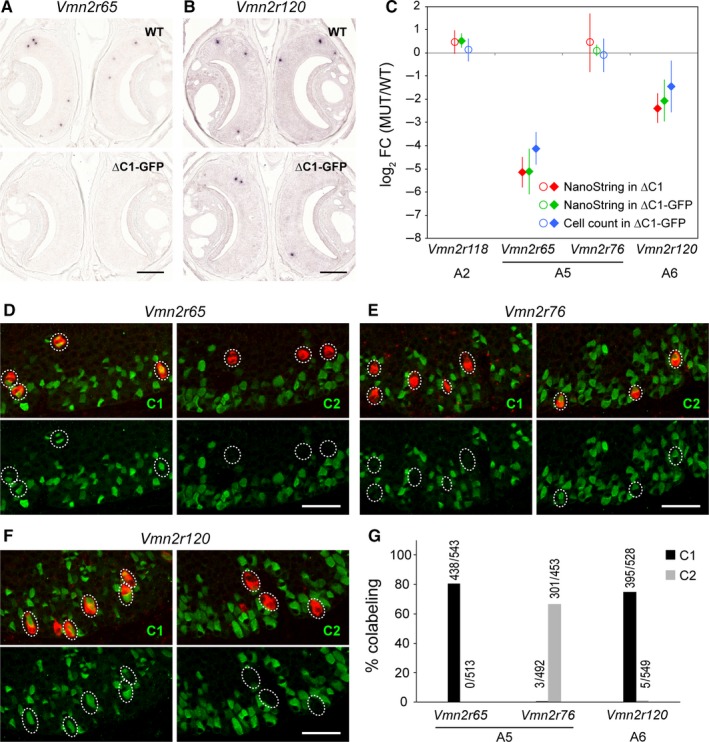
Reclassification of Vmn2r65 and Vmn2r120 as C1 type of V2R genes. (A,B) ISH with gene‐specific probes for Vmn2r65 (A) and Vmn2r120 (B) on coronal VNO sections of WT and ∆C1‐GFP mice. Labeled cells were visualized chromogenically. Four 10‐week‐old male mice per genotype were used. Scale bar, 200 μm. (C) Comparison of NanoString counts with ISH cell counts. Filled diamonds indicate DE genes in NanoString analysis or a significant decrease in cell count by ISH. Open circles indicate non‐DE genes. Vmn2r65 and Vmn2r120 were decreased in MUT mice consistently in NanoString and ISH analyses, and to the same extent for each gene: The log2 FC values are close, and there is overlap of the error bars (±99% CI). By contrast, there was no difference in ISH counts using gene‐specific probes for Vmn2r118 and Vmn2r76 genes, consistent with NanoString results. (D–F) Colabeling of Vmn2r65 (D), Vmn2r76 (E), and Vmn2r120 (F) by fluorescence ISH (red) in combination with IHC using anti‐C1 or anti‐C2 antibodies (green) on coronal VNO sections of C57BL/6J mice at 10 weeks. Scale bar, 50 μm. (G) Summary of the combined ISH/IHC analysis. VNO sections from three 10‐week‐old C57BL/6J male mice were analyzed. Above each bar, the number of double‐labeled VSNs/number of VSNs labeled by ISH with a gene‐specific probe is shown. The majority of VSNs expressing Vmn2r65 or Vmn2r120 in ISH were colabeled with C1 antibody, thus reclassifying these genes as C1 type of V2Rs.
