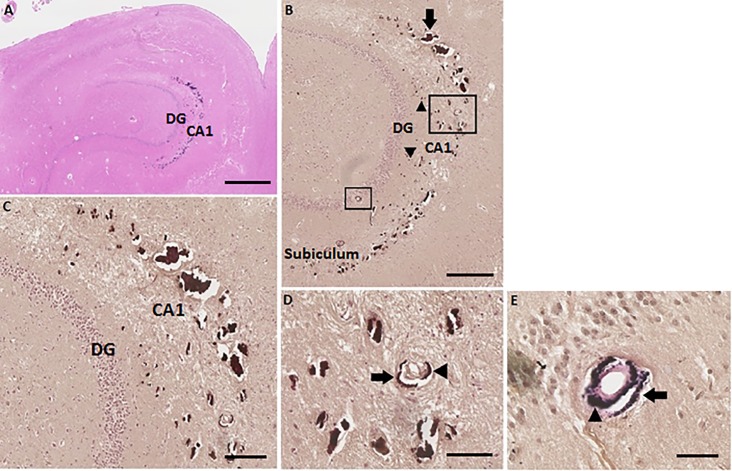
Fig 3. Severe calcifications in the tail of the left hippocampus (hippocampus number 1) of patient number 1 (as described in Tables 1 and 2).
(A) HE stain overview of the left hippocampal tail. Scale bar = 1 mm, 4x magnification. (B) Von Kossa-positive deposits in precapillaries and capillaries (arrowheads) in the molecular layer of the DG and CA1. Calcifications of the bigger vessels, mostly arteria (arrow), in the molecular layer of CA1 are clearly observed. Two arteria which are calcified are surrounded, one in the molecular layer of the CA1 and one in the granular layer of the DG. The calcifications spread out into the molecular layer of the subiculum. Scale bar = 600 μm, 10x magnification. (C) Zoomed in on the big calcifications of precapillaries, capillaries and bigger vessels in the molecular layer of the DG and CA1. Epithelial cells of the vascular wall are not seen, because of the big calcification deposits. Scale bar = 400 μm, 20x magnification. (D) Enlarged image of a von Kossa-positive calcified artery in the molecular layer of the CA1. Calcification of the tunica adventitia (arrow) and the tunica media (arrowhead) are identified. Scale bar = 200 μm, 40x magnification. (E) Calcified artery in the granular layer of the DG shown with Elastica van Gieson stain. Calcification of the tunica adventitia (arrow) and the tunica media (arrowhead) are identified. Scale bar = 100 μm, 40x magnification.