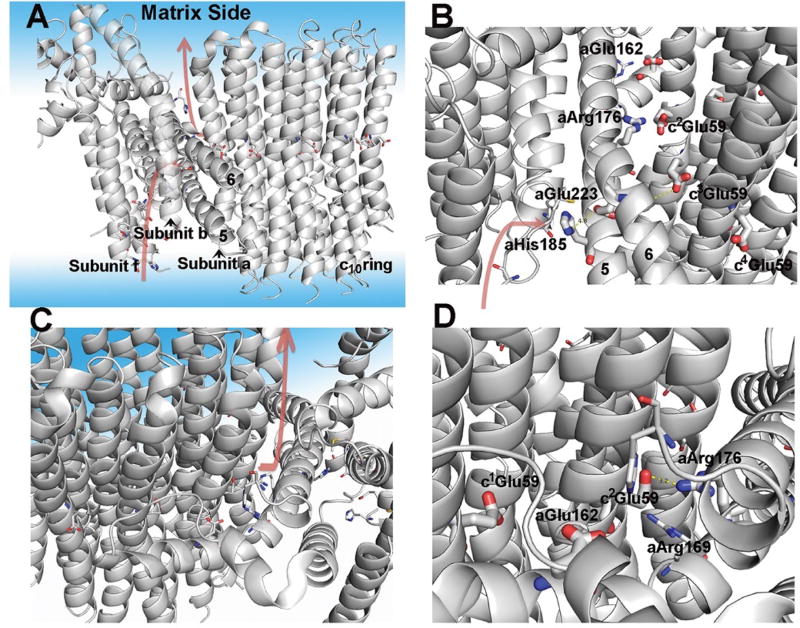
Fig. 4. Model of Fo and the proton pathways.
(A) Overall model of Fo with subunits a, b, c, and f displayed. The aqueous phase is also displayed with a light blue coloring. The postulated proton pathways for the entry from the intermembrane space and exit to the matrix are shown with the arrows. The protonation pathway during ATP synthesis is a path formed by subunits f, b, and a with the final course formed by helices 5 and 6 of a-subunit. (B) Side view of the entry pathway for protons during ATP synthesis with key residues indicated (see text for discussion). (C) Top side view of proton pathway for proton exit to the matrix. (D) View of proton pathway from the exit site showing helices 5 and 6 of a-subunit and the c-ring.