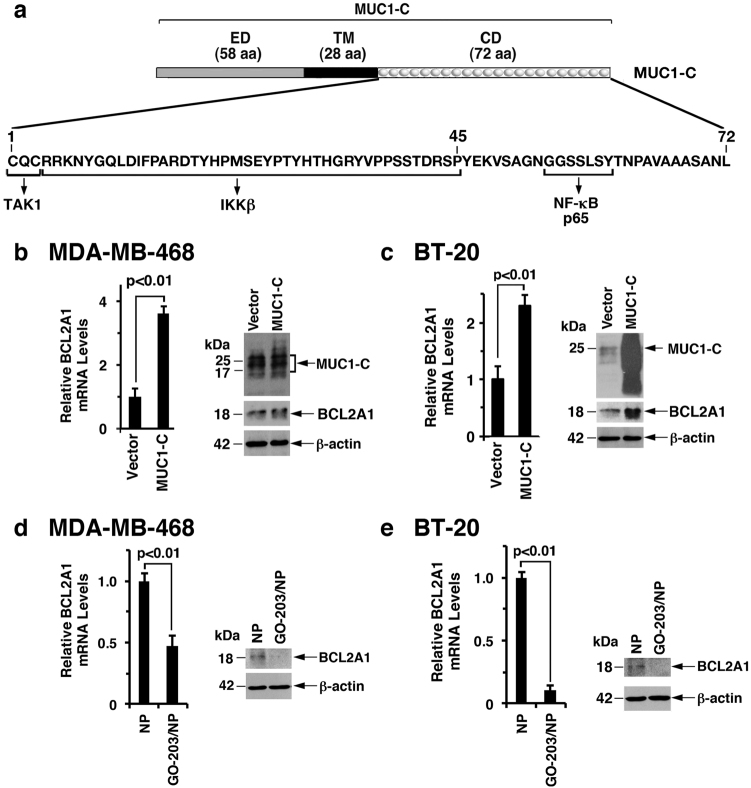
Fig. 2.
MUC1-C drives BCL2A1 expression. a Schema of the MUC1-C subunit with the sequence of the 72-amino acid intrinsically disordered cytoplasmic domain (CD). The CQC motif is required for MUC1-C homodimerization and is the target of GO-203. The MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain activates the inflammatory TAK1→IKK→NF-κB p65 pathway by direct interactions with these effectors. b, c MDA-MB-468 (b) and BT-20 (c) cells stably transduced to express a control or MUC1-C vector were analyzed for BCL2A1 mRNA levels by qRT–PCR. The results (mean ± SD of 3 determinations) are expressed as BCL2A1 mRNA levels relative to those in vector cells (assigned a value of 1) (left). Lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (right). d, e MDA-MB-468 (d) and BT-20 (e) cells treated with empty NPs or 7.5 μM GO-203/NPs for 5 d were analyzed for BCL2A1 mRNA levels by qRT–PCR. The results (mean ± SD of three determinations) are expressed as BCL2A1 mRNA levels relative to those in cells treated with empty NPs (assigned a value of 1) (left). Lysates from cells treated with empty NPs or 7.5 μM GO-203/NPs for 7 d were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (right)