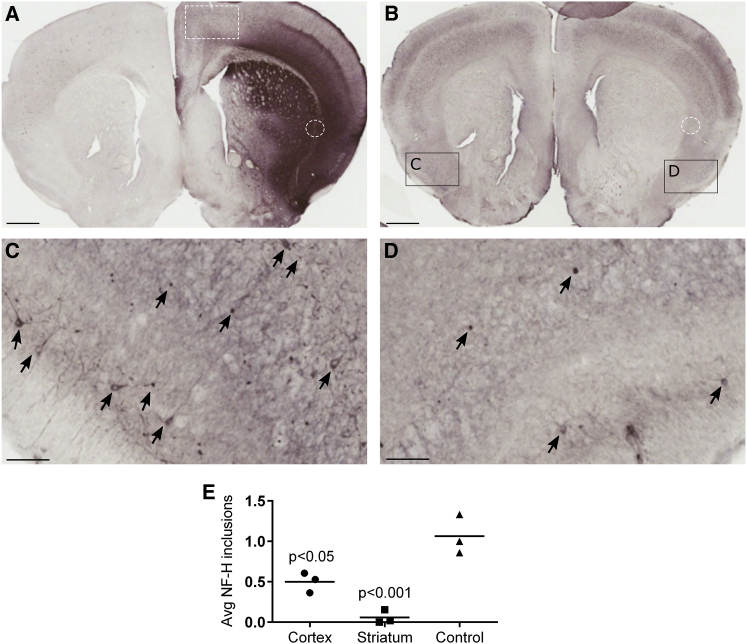
Figure 3.
AAV9/JeT-GAN Reduces NF Inclusions in Cortical and Striatal Neurons
Twenty-month-old GAN/Y KO mice received a unilateral brain injection into the border of the striatum and cortex of a mix of AAV9/JeT-FLAG-GAN and AAV9/JeT-GFP and harvested 4 weeks post-injection (cohort 1). (A) A representative image of GFP staining shows that AAV9 vector spread decreased with distance from the injection site and was substantially reduced in the uninjected hemisphere. The white hashed box outlines the “control” area that was not efficiently transduced by AAV9, and the white dashed circle shows the injection site. (B) A representative image of NF staining shows that compared to the untreated hemisphere (C), NF inclusions are greatly reduced in the treated side (D). (E) Quantification of NF inclusions in the treated hemisphere, normalized to the number of inclusions in the corresponding area of the untreated hemisphere of each mouse. Data are means ± SEM for each group, n = 3 mice. One-way ANOVA with Bonferonni’s post-hoc analysis. (A and B) Scale bars represent 1 mm. (C and D) Arrows point to examples of NF inclusions, and scale bars represent 0.1 mm.