Figure 4.
IT Delivery of AAV9/JeT-GAN in GAN KO Mice Attenuates Rotarod Deficits
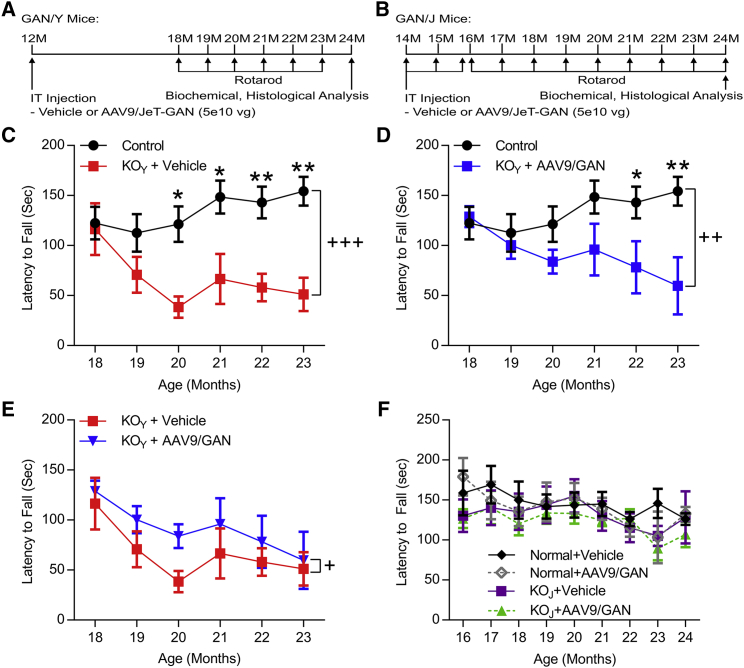
(A) Study design for GAN/Y KO (cohort 2) and (B) for GAN/J KO mice (cohort 3). (C) Aged GAN/Y KO mice (red) have significantly impaired rotarod performance as compared to normal control littermates (black) beginning at 20 months of age. (D) Treatment with AAV9/JeT-GAN delays a significant rotor deficit in GAN/Y KO mice (blue) as compared to normal control mice (black) until 22 months of age. (E) Over the course of testing, treatment with AAV9/JeT-GAN (blue) significantly improves rotarod performance as compared to vehicle-treated GAN KO mice (red). (F) No difference in rotarod performance was found between aged normal control (black) and vehicle-treated GAN/J KO mice (purple). Treatment with AAV9/JeT-GAN did not affect the motor performance of either control (gray) or GAN KO mice (green). Data are means ± SEM for each group (GAN/Y, n = 18 normal controls, 8 KO + vehicle, and 7 KO + AAV9/GAN; GAN/J, n = 10 normal + vehicle, 9 normal + AAV9/GAN, 10 KO + vehicle, and 11 KO + AAV9/GAN). Two-way ANOVA (age × group); main effect of group, +p < 0.05, ++p < 0.01, +++p < 0.001; Bonferonni’s post-hoc analysis of age: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.