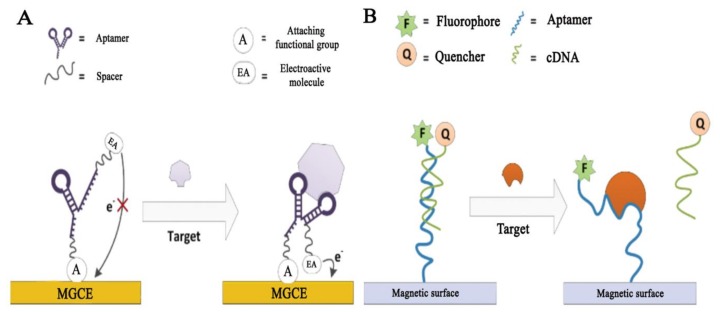
Figure 1.
(A) Target-induced structure switching (TISS) type of assay. Here, the interaction between an aptamer and a target molecule leads to change in the conformation of the aptamer. The conformational changes can be exploited for signal generation, e.g., by using an electroactive molecule (EA) fused to the aptamer. In the figure, MGCE is a magnetic glass carbon electrode; (B) Target-induced dissociation (TID) type of assay. Here, the aptamer is hybridized with a complementary oligonucleotide (cDNA). The interaction between a target molecule and an aptamer leads to release of the cDNA sequence from the aptamer. The release of the cDNA can provide different types of signals in different assay formats, in the given example FRET-is used for signal generation. Adapted from [3] with permission. Copyright 2014, De Gruyter.