Fig. 4.
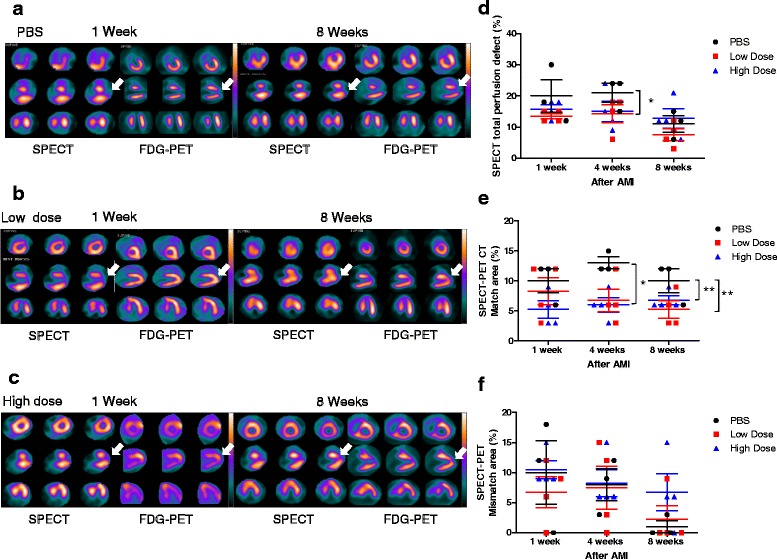
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) analysis demonstrates that intravenous injection of allogeneic UC-MSCs did not improve the myocardial perfusion defect but reduced the left ventricular nonviable myocardium area after acute myocardial infarction (AMI). a–c Representative SPECT and PET images at weeks 1 and 8. a Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) group: at week 1, SPECT reveals a moderate-severe perfusion defect at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead), and PET shows reduced fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead), demonstrating perfusion-metabolism match pattern, which reflects nonviable myocardium; at week 8, SPECT-PET shows the remaining perfusion-metabolism match pattern at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead). b Low-dose group: at week 1, SPECT shows a moderate-severe perfusion defect at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead), and PET demonstrates preserved FDG metabolism at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead), showing perfusion-metabolism mismatch pattern, which reflect viable myocardium; at week 8, SPECT-PET shows improvement in myocardial perfusion and FDG metabolism at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead). c High-dose group: at week 1, SPECT reveals a moderate-severe perfusion defect at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead), and PET shows increased FDG uptake at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead), demonstrating perfusion-metabolism mismatch pattern, which reflects viable myocardium; at week 8, SPECT shows the remaining perfusion defect at the apex and anterior wall apical segment, and PET shows increased FDG uptake at the apex and anterior wall apical segment (arrowhead), revealing perfusion-metabolism partial mismatch pattern, which expresses partial viable myocardium. d Bar chart percentage of SPECT perfusion defect shows that the cardiac perfusion defect was lower in the low-dose group compared with the PBS group at week 4. However, no significant difference was identified between groups at week 8. e Percentage of matched segments between SPECT and PET shows lower infarct size in UC-MSC-treated animals groups compared with the PBS group. f Percentage of mismatched segments between SPECT and PET showed no significant difference between the three groups. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. PBS group, n = 3; low-dose group, n = 4; and high-dose group, n = 4. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01
