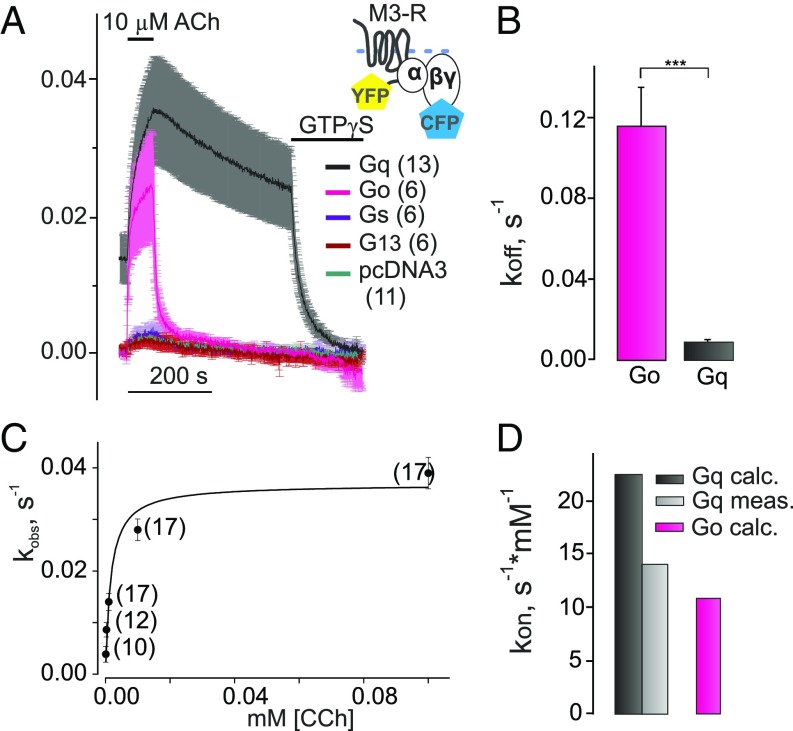
Fig. 2.
Selectivity of G protein binding to M3–R. (A) Agonist-dependent association and dissociation of M3–R with Go, Gq, Gs, or G13 proteins were measured after nucleotide depletion by means of FRET similar to that described in Fig. 1F. Average traces of YFP/CFP emission ratio (normalized to initial values) reflecting FRET between YFP-labeled M3–R and CFP-labeled Gγ2 subunit are illustrated when Gαo-WT (pink curve), Gαq-WT (black), Gs (purple), G13 (red), or empty pcDNA3 (dark green) was cotransfected. A much faster decay of the FRET signal after withdrawal of agonist was detected for Go proteins compared with Gq. (B) The constants of dissociation (koff; s−1) for Go and Gq proteins from M3–R are shown (magenta, n = 14; black, n = 30, respectively). (C) Observed association kinetics (kobs; s−1) of Gq protein with M3–R under GTP-depleted conditions were plotted over different CCh concentrations and fitted by a hyperbolic function. (D) Measured kon value of M3–R–Gq association kinetics (light gray, Gq meas.) obtained from fitted hyperbolic function using Eq. 2 compared with of Gq (black, Gq calc.) and Go (magenta, Go calc.), which were calculated based on steady-state experiments data as shown in Eq. 3. All data are plotted as means ± SEM for each condition; n of each experiment is shown in parentheses if not indicated. Statistical anlysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Student’s t test (***P <0.001).