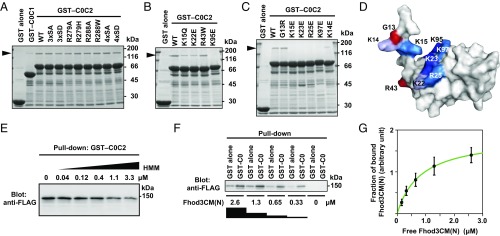
Fig. 3.
Specific interaction of the C0 domain of cMyBP-C with Fhod3. (A–C) Effect of amino acid substitutions on the interaction of C0C2 with the N-terminal region of Fhod3. FLAG-tagged Fhod3CM(N) in the lysate of HEK-293F cells was incubated with GST-fused C0C2 fragment carrying the indicated amino acid substitution: 3xSA, the S281A/S290A/S310A substitution; 4xSA, the S281A/S290A/S310A/S315A substitution. Proteins were pulled down with glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads. Precipitated proteins were subjected to SDS/PAGE and stained with CBB. The arrowheads indicate the position of Fhod3CM(N). (D) Mapping of the residues responsible for the Fhod3 interaction on the surface of the C0 domain. The figure is drawn using PyMOL from the structure at PDB ID code 2K1M (28). Amino acid residues responsible for the interaction with Fhod3 in B and C are shown in blue, and residues associated with cardiomyopathy are shown in red. (E) Competitive effects of heavy meromyosin on Fhod3 binding to cMyBP-C–C0C2. GST–cMyBP-C–C0C2 was incubated with the lysate of HEK-293F cells expressing FLAG-tagged Fhod3CM(N) (final concentration of 2.0 μM) in the presence of various concentration of heavy meromyosin. (F) Representative pull-down assay for quantification of binding between cMyBP-C–C0 and Fhod3CM(N). GST–cMyBP-C–C0 or GST alone immobilized to glutathione particles was incubated with the indicated concentrations of the lysate of HEK-293F cells expressing FLAG-tagged Fhod3CM(N). To avoid disturbing the binding equilibrium, bound Fhod3CM(N) were analyzed directly without washing by immunoblot with the anti-FLAG antibodies followed by fluorescence measurement. (G) Quantitative analysis for binding of cMyBP-C–C0 to Fhod3CM(N). Fractions of specifically bound Fhod3-N were determined as fraction bound to GST–C0 minus fraction to GST alone in F.