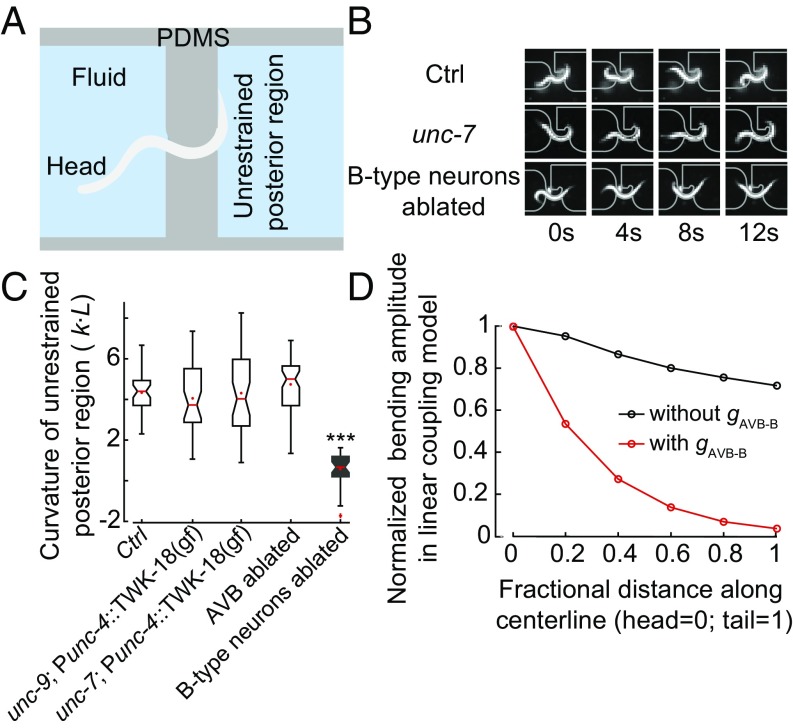
Fig. 2.
UNC-7– and UNC-9–dependent gap junctions are not required for proprioceptive couplings in the forward motor circuit. (A) Schematics of the microfluidic device for constraining a body segment with defined curvature. (B) Time-lapse video images of control (Upper), unc-7 (Middle), and B-type neurons ablated (Lower) worms trapped in the microfluidic device. In both control and unc-7 mutant animals, the posterior unrestrained body region followed the curvature of the channel. However, this was not the case when B-type motor neurons were optogenetically ablated. (C) In AVB-B gap junction-deficient mutants, or AVB-ablated worms, the posterior unrestrained body region also followed the curvature of the channel. Boxes indicate Q1 to Q3, error bars represent Q1 − 1.5IQR and Q3 + 1.5IQR, respectively, and notches indicate 95% confidence interval. ***P < 0.0001, compared with other strains, by Mann–Whitney U test. Control [N2; Punc-4::TWK-18(gf)], n = 40 measurements, 8 worms; unc-7 [unc-7; Punc-4::TWK-18(gf)], n = 41 measurements, 12 worms; unc-9 [unc-9; Punc-4::TWK-18(gf)], n = 38 measurements, 9 worms; AVB-ablated [Plgc-55(B)::miniSOG], n = 60 measurements, 10 worms; B-ablated (Pacr-5::miniSOG), n = 33 measurements, 9 worms. (D) In the linear model, incorporating the AVB-B gap junction inputs further deteriorated bending wave propagation.