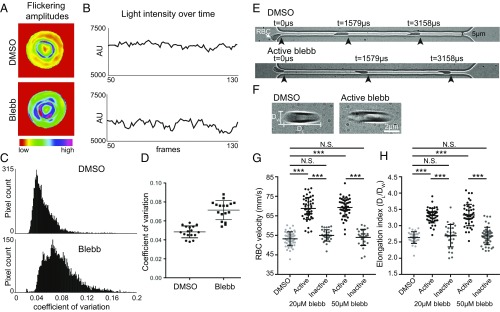
Fig. 5.
NMIIA motor activity controls the amplitude and variability of RBC membrane flickering and RBC deformability during flow in microchannels. (A–D) Human RBCs were treated with 5 μM blebbistatin or DMSO. (A) Color-coded representations of whole-RBC flickering amplitudes in representative cells, where red represents amplitude changes near zero and purple represents maximum changes. The blebbistatin-treated cell has higher flickering amplitudes throughout the cell. (B) Changes in light intensity over time in an area of 3 × 3 pixels in representative cells, as recorded by phase-contrast microscopy. The area from the blebbistatin-treated cell has larger changes in light intensity. (C) Frequency distributions of the coefficients of variation in all pixel amplitudes from representative cells. The blebbistatin-treated cell has more pixels with high coefficients of variation. (D) Coefficients of variation of membrane flickering amplitudes (n = 15 RBCs per treatment condition). (E and G) Treatment with active blebbistatin, but not inactive blebbistatin or DMSO, increases the velocity of RBCs flowing through a 5-μm-wide channel, corresponding to an increase in deformability. Representative cells are shown in E. Cells from two to three individual donors (***P < 0.0001) are shown in G: DMSO (n = 48), 20 μM active blebbistatin (n = 48), 20 μM inactive blebbistatin (n = 30), 50 μM active blebbistatin (n = 47), and 50 μM inactive blebbistatin (n = 28). Data are presented as mean ± SD for each condition. (F and H) Treatment with active, but not inactive, blebbistatin or DMSO increases the shear-induced elongation index as RBCs flow through a 20-μm-wide constriction in a 30-μm-wide channel, corresponding to an increase in deformability. Representative cells are shown in F. Cells from two to three individual donors (***P < 0.0001) are shown in H: DMSO (n = 30), 20 μM active blebbistatin (n = 45), 20 μM inactive blebbistatin (n = 30), 50 μM active blebbistatin (n = 45), 50 μM inactive blebbistatin (n = 45). Data are presented as mean ± SD for each condition.