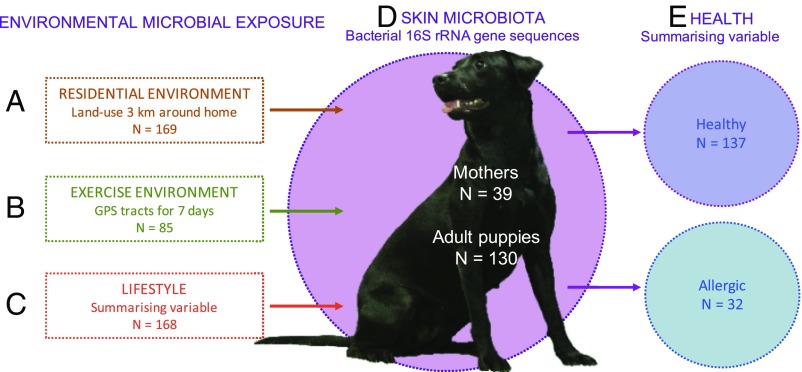
Fig. 1.
Exposure to environmental microbes is affected by three factors: where one lives (A), where one moves (B), and how one lives (C). We quantified these factors and studied their effects on the skin microbiota (D) and allergic symptoms (E) in dogs. The biodiversity hypothesis (42) suggests that the exposure to natural environments defines our microbial exposure (A–C), which in turn affects the composition of individual microbiota (D), and can relate to the development of inflammatory disorders (E) through immune modulation. Image courtesy of Aki Korhonen and Varpu Halonen (Foto Elukka, Lievestuore, Finland).